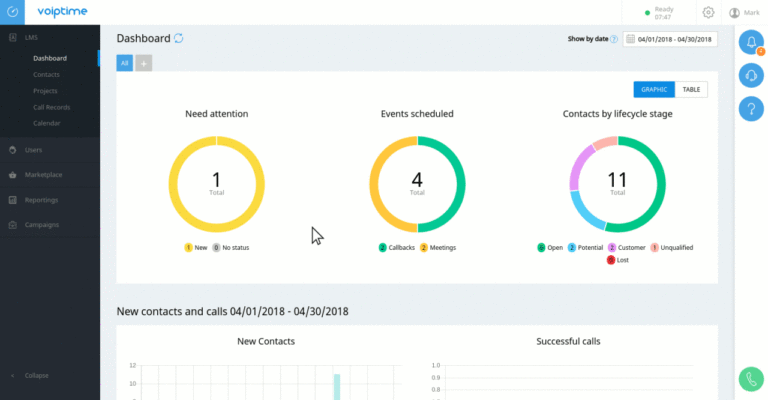
CRM solutions for insurance companies are revolutionizing how insurers interact with clients and manage their operations. No longer just contact management tools, modern CRMs offer powerful features for policy management, claims processing, and sales pipeline optimization, ultimately boosting efficiency and customer satisfaction. This exploration dives into the various types of CRM systems, their key features, integration challenges, and the crucial role they play in enhancing the overall customer experience and achieving a significant return on investment.
From cloud-based solutions offering scalability and accessibility to on-premise systems prioritizing data security, the choice of CRM depends heavily on the specific needs of the insurance company. Factors such as company size, existing IT infrastructure, and the type of insurance offered (life, property & casualty, health) all play a significant role in determining the optimal CRM solution. This analysis will unpack these considerations, providing a clear understanding of how the right CRM can transform an insurance business.
Types of CRM Solutions for Insurance
Choosing the right CRM is crucial for insurance companies to manage customer relationships effectively, improve operational efficiency, and ultimately boost profitability. The type of CRM system best suited for an insurance company depends heavily on factors like budget, company size, technical expertise, and the specific needs of its various departments. Let’s explore the main options.
Cloud-Based CRM Systems for Insurance
Cloud-based CRMs offer a subscription-based model where the software and data are hosted on the vendor’s servers. This eliminates the need for on-site infrastructure and IT maintenance, making it a cost-effective and scalable solution for many insurers.Advantages include reduced upfront costs, easy accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, automatic updates and backups, and enhanced scalability to accommodate business growth.
Disadvantages can include dependence on internet connectivity, potential security concerns related to data storage outside the company’s direct control, and possible vendor lock-in. For example, a sudden change in the vendor’s pricing or service could significantly impact the insurance company’s operations.
On-Premise CRM Systems for Insurance
On-premise CRM systems are installed and maintained on the insurance company’s own servers. This gives the company complete control over its data and infrastructure.Advantages include greater control over data security and customization options, potential for better performance in situations with limited or unreliable internet access, and the ability to integrate with existing legacy systems more easily. Disadvantages include high upfront investment in hardware and software, ongoing maintenance costs, the need for in-house IT expertise, and limited scalability compared to cloud-based solutions.
The initial investment can be substantial, requiring a significant capital outlay.
Hybrid CRM Systems for Insurance
Hybrid CRM systems combine elements of both cloud-based and on-premise solutions. This approach allows companies to leverage the benefits of both models, potentially mitigating some of their respective drawbacks.For example, sensitive customer data might be stored on-premise for enhanced security, while less critical data and functionalities are hosted in the cloud for scalability and accessibility. Advantages include flexibility, improved security for sensitive data, and cost-effectiveness compared to a purely on-premise solution.
Disadvantages include increased complexity in managing both on-premise and cloud components, and the potential for integration challenges between the two systems. Careful planning and integration expertise are essential for a successful hybrid deployment.
Comparison of Insurance CRM Solutions
The choice of a specific CRM solution depends on the unique requirements of the insurance company. Below is a comparison of four popular options, keeping in mind that features and pricing can change:
| CRM Solution | Key Features | Pricing Model | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce Financial Services Cloud | Policy management, claims processing, customer service tools, reporting and analytics | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Large insurance companies with complex needs |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Finance and Operations | Comprehensive financial management, integrated CRM capabilities, robust reporting | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Mid-sized to large insurance companies needing strong financial integration |
| Pega Insurance | Policy administration, claims management, customer engagement, AI-powered insights | Subscription-based, customized pricing | Companies seeking advanced automation and AI capabilities |
| Insly | Policy administration, claims management, client portal, integrations with other insurance systems | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Smaller to mid-sized insurance companies seeking a user-friendly solution |
CRM Solutions for Different Insurance Sectors
Different insurance sectors have unique needs. A life insurance company, for instance, requires a CRM that effectively manages long-term customer relationships, tracks policy anniversaries, and facilitates efficient communication regarding policy renewals and benefits. Property and casualty insurers need systems that streamline claims processing, manage policy documentation efficiently, and handle interactions related to incidents and damage assessments. Health insurance companies focus on managing member benefits, processing claims related to medical services, and maintaining HIPAA compliance.
A CRM tailored to each sector’s specific requirements ensures optimal efficiency and customer satisfaction. For example, a life insurance CRM might prioritize features related to long-term policy management and financial planning, while a P&C CRM would emphasize claims processing and rapid response to incidents.
Key Features of Insurance CRM Systems
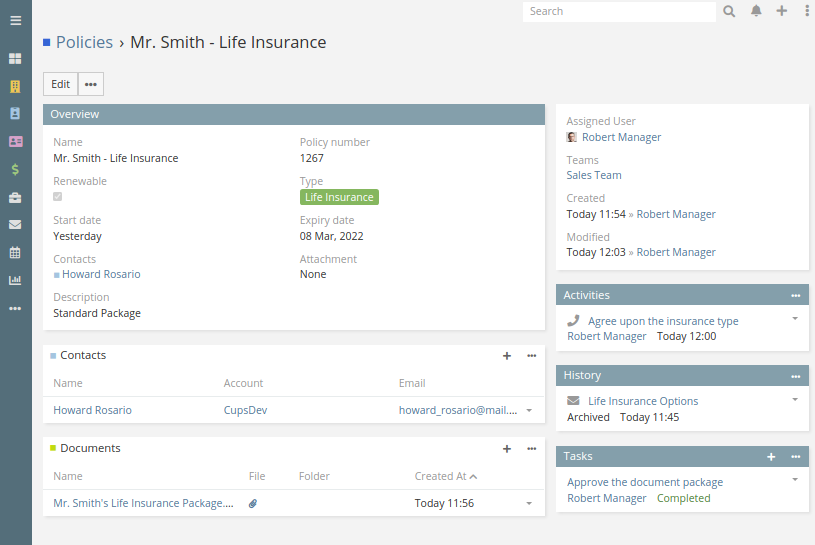
Insurance CRM systems are far more than just contact databases; they’re powerful tools designed to streamline every aspect of an insurance business, from lead generation to claims settlement. Effective CRMs integrate various functionalities to improve efficiency, enhance customer relationships, and ultimately boost profitability. This section delves into the key features that make these systems indispensable for modern insurance companies.Policy Management is CrucialEffective policy management is the backbone of any successful insurance operation.
A robust CRM system should seamlessly integrate all aspects of the policy lifecycle, minimizing manual processes and reducing errors. This integration significantly improves operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Policy Management Features
Policy creation within an insurance CRM often involves automated workflows, allowing for quick and accurate policy generation based on client data and selected coverage options. Renewal tracking provides automated reminders and alerts, minimizing the risk of lapsed policies and ensuring consistent revenue streams. Furthermore, claims processing integration allows for easy access to claim information, reducing processing times and improving communication with clients.
This feature often includes automated workflows to manage the claim process from initiation to settlement. For example, a system might automatically route a claim to the appropriate adjuster based on policy type and location, while also sending notifications to the policyholder at each stage of the process. This integrated approach eliminates the need for manual data entry and improves accuracy, leading to faster claim resolutions and increased customer satisfaction.
Lead Nurturing Workflow
The following diagram illustrates a typical lead nurturing workflow within an insurance CRM system:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with a “Lead Acquisition” box (e.g., from website form, referral). This would flow to a “Lead Qualification” box (e.g., determining needs and risk profile). Next would be a “Communication & Engagement” box (e.g., personalized emails, phone calls).
Following that would be a “Proposal & Presentation” box (e.g., tailored insurance options). Then, a “Closing & Onboarding” box (e.g., policy signing and setup). Finally, an “Ongoing Relationship Management” box (e.g., renewal reminders, proactive service). Arrows would connect each box, showing the progression of the lead through the sales funnel.]
Essential Reporting and Analytics Features
Effective data analysis is vital for informed decision-making within the insurance industry. Insurance-focused CRM solutions provide a range of reporting and analytics features designed to provide valuable insights into business performance and customer behavior.
- Sales Performance Reporting: Tracks key sales metrics such as conversion rates, average policy value, and sales cycle length. This allows insurers to identify areas for improvement in their sales process and target high-potential leads more effectively. For example, an insurer might use this data to identify which marketing channels are generating the most qualified leads or to optimize their sales scripts based on performance analysis.
- Customer Segmentation: Groups customers based on shared characteristics (demographics, policy type, claims history) to enable targeted marketing and personalized service. This allows for more efficient resource allocation and improved customer retention. For instance, an insurer could segment their customer base by age to offer tailored products or services, such as bundled packages for seniors or specialized coverage for young drivers.
- Claim Analysis: Tracks claim frequency, severity, and cost to identify trends and potential areas of risk. This enables proactive risk management and improved pricing strategies. A company might use claim data to identify specific areas where fraud is more prevalent or to adjust premiums based on regional risk factors.
- Policy Renewal Forecasting: Predicts future policy renewals to better manage cash flow and proactively address potential lapses. This data allows for targeted retention campaigns and improved financial planning. For example, an insurer could identify policies nearing renewal and proactively reach out to customers to discuss their needs and offer renewal incentives.
- Agent Performance Tracking: Monitors individual agent productivity, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction scores to identify top performers and areas needing improvement. This enables effective performance management and targeted training programs. An insurer could use this data to reward high-performing agents or provide additional training to those struggling to meet their targets.
Integration with Existing Insurance Systems
Integrating a CRM system into an insurance company’s existing technological infrastructure is crucial for maximizing efficiency and data utilization. A successful integration streamlines workflows, improves customer service, and provides a holistic view of the customer journey. However, the process can be complex, demanding careful planning and execution to avoid disruption and ensure a smooth transition.The primary methods for integrating a CRM with existing systems—policy administration, billing, and claims management—generally fall into three categories: direct database integration, middleware solutions, and API-driven integrations.
Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages, making the optimal choice dependent on the specific needs and technical capabilities of the insurance company.
Methods for Integrating CRM with Insurance Systems
Direct database integration involves establishing a direct connection between the databases of the CRM and the other systems. This approach offers high performance and tight data synchronization but requires significant technical expertise and can be risky if not implemented carefully. Changes to the database structure in one system might necessitate corresponding changes in others, leading to potential downtime and data inconsistencies.
Middleware solutions, on the other hand, act as intermediaries, translating data between systems with different formats and protocols. This approach offers greater flexibility and reduces the risk of direct database conflicts, but can introduce performance overhead. Finally, API-driven integrations utilize application programming interfaces to facilitate data exchange. This method is increasingly popular due to its flexibility, scalability, and relative ease of implementation.
APIs allow for modular integration, enabling companies to connect and disconnect systems as needed, making it easier to adapt to changing business requirements.
Challenges of Integrating with Legacy Systems
Integrating a new CRM with legacy insurance systems often presents significant challenges. Legacy systems are typically built on outdated technologies and may lack the necessary APIs or standardized data formats for seamless integration. Data inconsistencies between the systems can also be a major hurdle. Furthermore, the complexity of legacy systems can make it difficult to understand the data flow and identify potential points of failure.
To mitigate these challenges, a phased approach to integration is often recommended. This involves prioritizing the most critical integrations first and gradually adding more systems as the integration process is refined. Data cleansing and standardization are also essential steps to ensure data quality and consistency. Investing in skilled personnel with expertise in both legacy systems and modern CRM technologies is also crucial for a successful integration.
Careful planning, robust testing, and change management are vital components in mitigating risks. Consider pilot programs with a subset of data to validate the integration process before a full-scale rollout.
API-Driven Data Exchange, CRM solutions for insurance companies
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the backbone of modern system integration, particularly when dealing with diverse technologies. They enable secure and efficient data exchange between the CRM and other key insurance platforms. For instance, an API can automatically update customer information in the CRM whenever a policy is issued or modified in the policy administration system. Similarly, APIs can pull claims data from the claims management system, providing a comprehensive view of customer interactions and claims history within the CRM.
This real-time data flow eliminates manual data entry, reducing errors and saving time. A well-designed API architecture should support both inbound and outbound data flows, ensuring that information flows seamlessly between systems. Consider using RESTful APIs for their flexibility and widespread adoption in the industry. Robust error handling and security measures, such as authentication and authorization, are also crucial to ensure data integrity and security.
The selection of appropriate API protocols and data formats (like JSON or XML) are critical aspects of the design process, impacting efficiency and interoperability.
Improving Customer Experience with CRM
A well-implemented CRM system is more than just a database; it’s a powerful tool for transforming the customer experience within the insurance industry. By centralizing customer information and automating processes, CRM solutions enable insurers to personalize interactions, anticipate customer needs, and resolve issues efficiently, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction and retention. This translates directly to a healthier bottom line.CRM systems dramatically improve customer retention through personalized communication and proactive service.
Instead of generic email blasts, CRM allows insurers to segment their customer base based on factors like policy type, claims history, and demographics. This enables targeted marketing campaigns and personalized communication, making customers feel valued and understood. Proactive service, such as automated reminders for policy renewals or personalized advice based on risk profiles, further strengthens the customer relationship and reduces churn.
For example, a CRM system might identify customers nearing the end of their policy term and automatically send them a renewal offer tailored to their specific needs, including potential discounts or upgrades.
Streamlining the Claims Process with CRM Features
CRM systems offer several features that streamline the claims process, significantly enhancing customer satisfaction. Automated workflows can guide claims through each stage, from initial reporting to final settlement, ensuring timely processing and reducing delays. Centralized communication ensures all parties involved – the customer, adjusters, and other relevant personnel – have access to the same information, preventing confusion and misunderstandings.
Real-time tracking allows customers to monitor the progress of their claims online, providing transparency and reducing anxiety. For instance, a customer can log in to a portal and see the exact status of their claim, including the date each step was completed and who is currently handling it. This level of visibility significantly improves the customer experience, contrasting sharply with the often opaque and frustrating traditional claims process.
Best Practices for Enhancing Customer Experience with CRM Data
Effective utilization of CRM data is key to maximizing its impact on customer experience. Here are some best practices:
- Data Quality is Paramount: Ensure data accuracy and completeness. Regular data cleansing and validation are crucial. Inaccurate information leads to poor decision-making and frustrated customers.
- Leverage Data Analytics: Use CRM analytics to identify customer trends, preferences, and pain points. This data-driven approach allows for proactive improvements to products and services.
- Personalize Interactions: Use customer data to personalize communication and offers. This demonstrates that you understand and value individual customer needs.
- Empower Employees: Equip employees with the right tools and training to effectively utilize CRM data to provide excellent customer service. A well-trained staff is essential for successful CRM implementation.
- Integrate with Other Systems: Integrate your CRM system with other relevant systems, such as policy administration and claims processing systems, to ensure a seamless flow of information.
- Regularly Review and Refine: Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your CRM strategy. Adapt and improve your approach based on customer feedback and performance data. A static CRM strategy will quickly become obsolete.
Security and Compliance Considerations: CRM Solutions For Insurance Companies
Implementing a CRM for an insurance company requires a robust approach to security and compliance. The sensitive nature of the data handled – personal information, financial details, medical history – necessitates stringent measures to protect customer privacy and adhere to relevant regulations. Failure to do so can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.The importance of data security and compliance cannot be overstated.
Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States impose strict rules on how personal and health information is collected, stored, and processed. Insurance companies must ensure their CRM systems are fully compliant with these and other applicable laws, demonstrating a commitment to responsible data handling.
This goes beyond simply installing software; it requires a comprehensive strategy encompassing technology, processes, and employee training.
Data Encryption and Access Controls
Data encryption is a cornerstone of data security. This involves converting data into an unreadable format, rendering it useless to unauthorized individuals even if accessed. Insurance companies should employ strong encryption methods, both at rest (when data is stored) and in transit (when data is being transferred). For example, using AES-256 encryption for data at rest and TLS/SSL for data in transit is considered industry best practice.
Furthermore, robust access controls limit who can view and modify specific data within the CRM. Role-based access control (RBAC) is a common approach, assigning different levels of access based on an employee’s role and responsibilities. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information, minimizing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. For instance, a claims adjuster might have access to claim details, but not to policyholder’s financial information unrelated to the claim.
Regular audits of access logs help to identify and address any suspicious activity.
Security Measures for Protecting Sensitive Customer Data
Several key security measures are crucial for safeguarding customer data within an insurance CRM. These include:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple forms of authentication (e.g., password and a one-time code from a mobile app) significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized logins.
- Regular security audits and penetration testing: Independent assessments identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system, allowing for proactive remediation.
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS): These systems monitor network traffic and system activity for malicious behavior, alerting administrators to potential threats in real-time.
- Data loss prevention (DLP) tools: DLP solutions prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control, whether intentionally or accidentally, through measures like blocking unauthorized downloads or email attachments.
- Employee training and awareness programs: Educating employees about security best practices, such as phishing awareness and password management, is crucial to prevent human error, a major cause of data breaches. Regular training should reinforce these principles and address emerging threats.
Implementing these measures creates a layered security approach, making it significantly more difficult for attackers to breach the system and access sensitive data. The combination of strong technical controls and a security-conscious workforce is essential for maintaining data confidentiality and integrity.
Return on Investment (ROI) of Insurance CRM

Implementing a CRM system represents a significant investment for any insurance company. However, the potential return on that investment can be substantial, impacting everything from sales figures to employee efficiency and customer loyalty. Understanding how to measure and maximize this ROI is crucial for justifying the initial expense and ensuring long-term success. This section details methods for calculating ROI and provides a hypothetical example to illustrate its potential benefits.Measuring the ROI of a CRM system isn’t a simple calculation; it requires a multifaceted approach considering various tangible and intangible benefits.
It’s not just about the immediate cost savings; it’s about the long-term impact on profitability and competitive advantage. A comprehensive assessment should encompass improved sales, reduced operational costs, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased employee productivity.
Methods for Measuring Insurance CRM ROI
Several key performance indicators (KPIs) can be used to quantify the return on investment from a CRM system. These metrics allow insurance companies to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate the value of the system to stakeholders.
- Increased Sales Revenue: Track the increase in sales generated through improved lead management, targeted marketing campaigns, and enhanced customer relationships facilitated by the CRM. This can be measured by comparing sales figures before and after CRM implementation, focusing on metrics such as closed-won deals, average deal size, and conversion rates.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Analyze how the CRM streamlines processes, reduces manual tasks, and minimizes errors. This could include decreased administrative overhead, reduced paperwork, faster claim processing, and improved agent efficiency. Quantify these savings by comparing operational expenses before and after implementation.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Measure customer satisfaction through surveys, feedback forms, and Net Promoter Score (NPS). A CRM system contributes to higher satisfaction through personalized communication, faster response times, and proactive service. Increased customer retention and positive word-of-mouth referrals are valuable indicators.
- Enhanced Employee Productivity: Evaluate how the CRM enhances agent productivity by tracking metrics like time spent on tasks, number of cases handled, and customer interactions. Improved data accessibility and streamlined workflows lead to increased efficiency and reduced employee burnout.
Hypothetical Scenario: Illustrating CRM ROI
Let’s consider “Acme Insurance,” a mid-sized company with 50 agents. Before implementing a CRM, Acme experienced an average of 20% customer churn annually, a 10% conversion rate on leads, and high administrative costs due to inefficient processes. After implementing a CRM system, Acme saw a 5% decrease in customer churn, a 20% increase in conversion rates, and a 15% reduction in administrative costs.
These improvements, combined with a 10% increase in average deal size due to better cross-selling opportunities, resulted in a significant increase in overall profitability. The investment in the CRM quickly paid for itself through increased revenue and reduced expenses.
Potential Cost Factors Associated with Insurance CRM Implementation and Maintenance
Implementing and maintaining a CRM system involves various costs that must be factored into the overall ROI calculation. Understanding these upfront will help insurance companies accurately project their return.
- Software Licensing Fees: These are recurring costs depending on the number of users and chosen features.
- Implementation Costs: This includes consulting fees, data migration, customization, and training.
- Hardware and Infrastructure Costs: This might involve upgrading servers or cloud storage.
- Integration Costs: Connecting the CRM to existing systems (like policy management or claims processing) can be complex and expensive.
- Maintenance and Support Costs: Ongoing maintenance, updates, and technical support are necessary.
- Employee Training Costs: Training agents and staff on how to effectively use the CRM is essential.
End of Discussion

Implementing the right CRM solution can be transformative for insurance companies, streamlining operations, improving customer relationships, and ultimately driving profitability. By carefully considering the various types of CRMs, integrating them seamlessly with existing systems, and prioritizing data security and compliance, insurance providers can leverage the power of CRM to enhance their business significantly. The key lies in understanding the unique needs of the business and selecting a solution that aligns perfectly with those requirements, maximizing both efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Clarifying Questions
What is the average cost of implementing a CRM for an insurance company?
The cost varies significantly depending on the size of the company, the chosen CRM system, and the level of customization required. Expect a range from a few thousand dollars for smaller, simpler systems to hundreds of thousands for enterprise-level solutions with extensive customization and integration.
How long does it typically take to implement a new CRM system?
Implementation timelines vary greatly, from a few weeks for simpler systems to several months or even years for complex enterprise deployments. Factors influencing this include system complexity, data migration requirements, and the level of employee training needed.
What are some common challenges faced during CRM implementation?
Common challenges include data migration issues, user adoption problems, integration complexities with existing systems, and the need for extensive employee training. Careful planning and change management are crucial for successful implementation.
Can a CRM system help with regulatory compliance?
Yes, many CRMs offer features to support regulatory compliance, such as data encryption, access controls, and audit trails. However, it’s crucial to select a CRM that specifically addresses the relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) for your company and region.
How can I measure the ROI of my CRM investment?
Measure ROI by tracking key metrics such as increased sales, improved customer retention rates, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Comparing these metrics before and after CRM implementation provides a clear picture of the return on investment.