Insurance Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is more than just software; it’s the backbone of a thriving insurance business. It’s about building genuine connections with clients, understanding their needs, and providing seamless, personalized service. From streamlining claims processes to proactively identifying high-value customers, effective CRM transforms how insurance companies operate and interact with their policyholders. This exploration delves into the multifaceted world of insurance CRM, examining its core components, strategic applications, and future implications.
We’ll cover everything from choosing the right CRM system for your specific needs (life, health, auto, etc.) to leveraging data analytics for smarter decision-making. We’ll also discuss the crucial aspects of compliance and security, ensuring you navigate the regulatory landscape with confidence. Ultimately, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge to build stronger customer relationships and drive sustainable growth in your insurance business.
Defining Insurance CRM
Insurance CRM (Customer Relationship Management) is a technology solution designed to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. It helps insurance companies streamline operations, improve customer service, and ultimately, boost sales and profitability. A robust CRM system provides a centralized hub for all customer information, allowing for personalized interactions and more efficient workflows.
Core Components of a Successful Insurance CRM System
A successful insurance CRM system relies on several key components working together. These include a comprehensive database storing all customer information (policy details, claims history, contact preferences, etc.), integrated communication tools (email, phone, chat), reporting and analytics dashboards providing insights into customer behavior and sales performance, and workflow automation features to streamline repetitive tasks like policy renewals or claims processing.
Crucially, the system should also offer seamless integration with other insurance-specific software, such as policy administration systems and claims management platforms. Without this integration, the CRM becomes an isolated data silo, losing its value.
Differences Between CRM Systems in Various Insurance Sectors
While the core principles of CRM remain consistent across different insurance sectors, specific functionalities and features often vary. For example, a life insurance CRM will heavily emphasize long-term relationship management, incorporating tools for tracking policy anniversaries and providing personalized financial planning support. In contrast, an auto insurance CRM might prioritize efficient claims processing and streamlined communication during accident reporting and repair stages.
Health insurance CRMs often include features for managing provider networks, coordinating care, and addressing member inquiries related to coverage and benefits. These sector-specific differences reflect the unique needs and customer interactions within each insurance vertical.
Examples of CRM Use in Insurance
Insurance companies leverage CRM systems in numerous ways to enhance customer interactions. Consider personalized marketing campaigns triggered by specific customer events, such as policy renewals or significant life changes (marriage, birth of a child). CRM data enables targeted communication, offering relevant products or services. Another example is improved customer service. Agents can access complete customer profiles instantly, providing accurate and efficient responses to inquiries.
Furthermore, CRM analytics can identify trends in customer complaints or claims, allowing companies to proactively address potential issues and improve their products or services. Proactive outreach to at-risk customers based on predicted churn is another powerful application.
Comparison of Leading Insurance CRM Software Solutions
| Feature | Software A (Example: Salesforce Financial Services Cloud) | Software B (Example: Microsoft Dynamics 365) | Software C (Example: Pega) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core CRM Functionality | Comprehensive contact management, lead tracking, sales force automation | Robust contact management, lead nurturing, opportunity management | Highly configurable, adaptable to specific insurance needs |
| Insurance-Specific Features | Policy management integration, claims processing tools | Strong reporting and analytics, integration with other Microsoft products | Advanced workflow automation, AI-powered insights |
| Pricing Model | Subscription-based, tiered pricing based on features and users | Subscription-based, tiered pricing based on features and users | Subscription-based, typically requires custom implementation and higher upfront costs |
| Integration Capabilities | Wide range of integrations with other systems | Seamless integration within the Microsoft ecosystem | Highly customizable integration options |
Enhancing Customer Engagement
Effective customer engagement is the lifeblood of any successful insurance business. A well-implemented CRM system is crucial for building strong, lasting relationships with policyholders, leading to increased retention and ultimately, profitability. By leveraging CRM’s capabilities, insurers can move beyond transactional interactions and cultivate genuine connections with their clients.
This section explores how CRM features can be used to significantly improve customer engagement throughout the entire customer lifecycle, from the initial contact to ongoing support and beyond. We’ll examine specific strategies for enhancing the customer experience and maximizing the value of your CRM investment.
Customer Onboarding Process Design
A streamlined and engaging onboarding process is critical for setting the right tone from the start. Using CRM, insurers can automate many aspects of this process, such as sending welcome emails, providing access to online portals, and scheduling introductory calls. This personalized approach ensures new customers feel valued and informed from day one. For example, an automated email sequence could include a welcome message, a policy summary, and a link to helpful resources, all triggered automatically upon policy activation within the CRM system.
This ensures consistency and reduces the manual workload on customer service representatives. Furthermore, the CRM can track completion of each step, allowing for quick identification of customers who may require additional support.
Personalizing Customer Communications
CRM data provides a wealth of information that can be used to personalize customer interactions. By segmenting customers based on demographics, policy type, claims history, and other relevant factors, insurers can tailor their communications to resonate with specific needs and preferences. For example, a customer who recently experienced a claim might receive a follow-up email expressing empathy and offering assistance with any outstanding questions.
Conversely, a long-term, low-risk customer might receive a personalized email highlighting loyalty benefits or exclusive offers. This targeted approach improves customer satisfaction and strengthens brand loyalty. Using CRM analytics, insurers can measure the effectiveness of different personalization strategies and continuously refine their approach.
Proactive Customer Service and Issue Resolution
CRM allows for proactive identification and resolution of potential customer issues. For instance, the system can flag customers nearing the renewal date of their policy, prompting agents to reach out and discuss renewal options. Similarly, CRM can track customer interactions and identify patterns that might indicate dissatisfaction or potential problems. This allows for timely intervention, preventing escalation of minor issues into major complaints.
For example, if a customer frequently contacts support regarding a specific feature of their policy, the CRM can alert the relevant team to investigate and provide targeted support or even product improvements. This proactive approach demonstrates a commitment to customer satisfaction and strengthens customer relationships.
Identifying and Nurturing High-Value Customers
CRM systems provide the tools to identify and nurture high-value customers. By analyzing customer data, insurers can pinpoint individuals who generate significant revenue or demonstrate high loyalty. These customers can then be targeted with personalized offers, exclusive services, and proactive support to foster deeper relationships. For instance, a customer with multiple policies and a long history of on-time payments could be offered a premium discount or an invitation to an exclusive client event.
This demonstrates appreciation for their loyalty and encourages continued business. Furthermore, CRM analytics can track the effectiveness of these nurturing strategies, enabling insurers to optimize their approach and maximize the return on investment.
Improving Operational Efficiency
Implementing a robust insurance CRM system significantly boosts operational efficiency, streamlining workflows and reducing manual effort. This leads to cost savings, faster response times, and improved customer satisfaction. Let’s explore how to maximize these benefits.
Effective CRM implementation requires careful consideration of key performance indicators (KPIs) and a well-defined workflow. Integration with existing systems is also crucial for a seamless operational flow.
Key Metrics for Measuring CRM Effectiveness
Tracking the right metrics provides crucial insights into CRM performance and identifies areas for improvement. These metrics should be regularly monitored and analyzed to ensure the system is delivering the expected ROI.
Some key metrics include:
- Policy issuance time: Measures the time taken from application to policy issuance. A decrease indicates improved efficiency.
- Claims processing time: Tracks the duration from claim submission to settlement. Faster processing times show improved efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Customer satisfaction scores (CSAT): Gauges customer happiness with the service received. High CSAT scores suggest effective CRM use.
- Number of customer interactions per case: A lower number indicates efficient handling of customer issues, reducing unnecessary contact.
- Agent productivity: Measures the number of tasks completed per agent, reflecting efficiency in handling customer interactions and tasks.
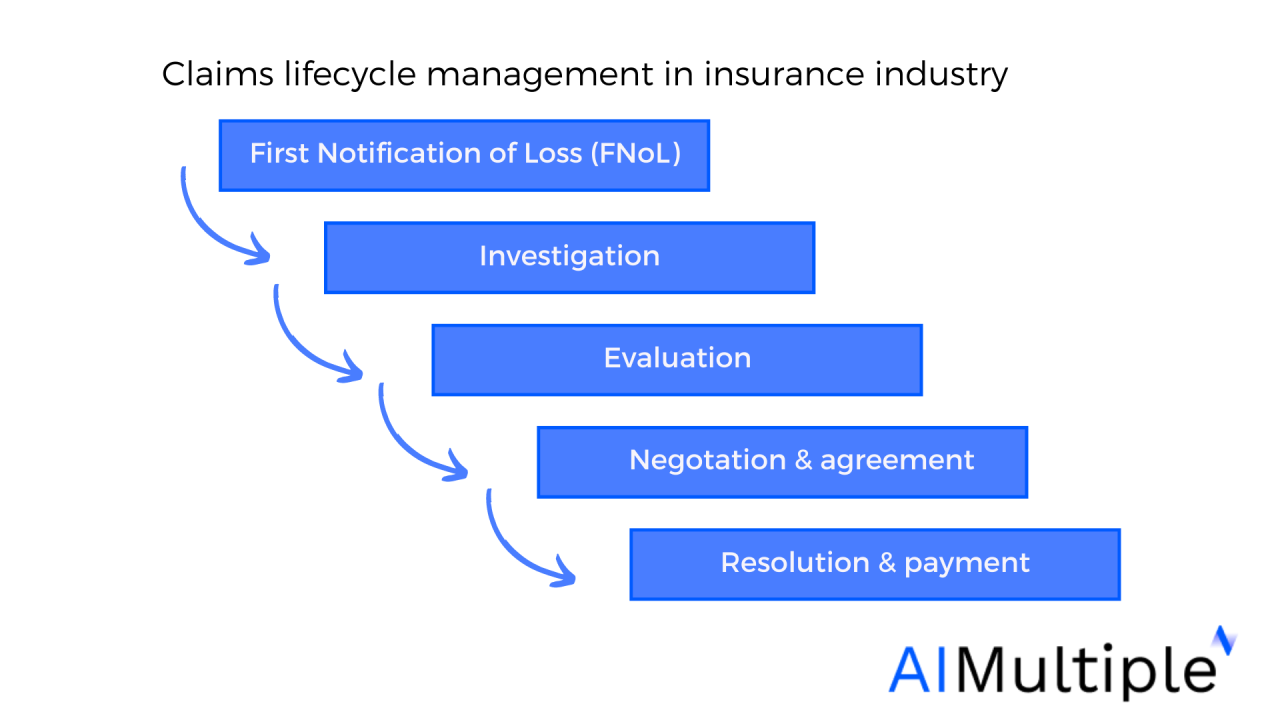
Workflow for Managing Insurance Claims Using CRM Functionalities
A well-structured claim management workflow within the CRM system is essential for quick and efficient processing.
The process could be organized as follows:
- Claim registration: The claim is logged in the CRM, automatically assigning it a unique ID and routing it to the appropriate adjuster.
- Initial assessment: The adjuster reviews the claim details and documents, initiating contact with the policyholder if needed.
- Investigation: The adjuster gathers further information, potentially involving third-party investigations.
- Claim evaluation: The adjuster determines the validity of the claim and the amount to be paid.
- Settlement: The payment is processed, and the claim is closed in the CRM system. The system automatically updates the policyholder’s status and records all communications.
Integrating CRM with Other Insurance Systems
Seamless integration with other insurance systems is vital for a truly effective CRM. This integration eliminates data silos and ensures information consistency across all platforms.
Key integrations include:
- Policy Administration System (PAS): Real-time access to policy details allows agents to quickly address customer inquiries and update information.
- Billing System: Automated updates to payment information and status provide a complete view of the customer’s financial relationship with the company.
- Claims Management System: Integration streamlines claim processing, reducing manual data entry and improving accuracy.
Process Map Illustrating CRM Streamlining of the Sales Process
A CRM system can significantly streamline the sales process by automating tasks, providing better lead management, and improving communication.
A simplified process map would look like this:
Stage 1: Lead Generation & Qualification
-Leads are captured through various channels (website forms, referrals, marketing campaigns). The CRM automatically qualifies leads based on pre-defined criteria.
Stage 2: Lead Nurturing
-Qualified leads are nurtured through automated email sequences and personalized communication, building relationships and educating them about the company’s offerings.
Stage 3: Sales Presentation & Proposal
-Sales agents leverage the CRM to access client information, prepare customized proposals, and schedule meetings.
Stage 4: Policy Issuance & Onboarding
-Once a sale is closed, the CRM automates the policy issuance process and facilitates onboarding, ensuring a smooth transition for the new customer.
Stage 5: Post-Sale Follow-up
-The CRM manages follow-up communications, ensuring customer satisfaction and identifying potential upselling opportunities.
Data Analysis and Reporting: Insurance Customer Relationship Management

Insurance CRM systems are data goldmines. The sheer volume of information they collect – from policy details and claims history to customer interactions and preferences – provides unparalleled opportunities for insightful analysis and strategic decision-making. Harnessing this data effectively is crucial for maximizing profitability and enhancing customer satisfaction.Effective data analysis within an insurance CRM allows insurers to move beyond simply storing information and instead use it to proactively manage risk, improve customer service, and optimize business operations.
This involves leveraging sophisticated reporting tools and analytical techniques to uncover hidden trends and patterns, leading to data-driven decisions that ultimately benefit both the company and its policyholders.
Insightful Reports Generated from CRM Data
A well-implemented CRM system can generate a wide variety of insightful reports. These reports can be tailored to specific business needs, providing key performance indicators (KPIs) across different departments. For example, a claims department might utilize reports analyzing average claim processing times, identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Sales teams can benefit from reports tracking lead conversion rates and identifying high-performing agents.
Furthermore, reports detailing customer churn rates can highlight areas needing attention in customer retention strategies. A comprehensive report could show the average claim cost per policy type, segmented by age group and location, revealing potential risk factors for future pricing models. Another report could track customer satisfaction scores over time, identifying trends and potential issues.
Identifying Customer Trends and Patterns
CRM data allows for the identification of key customer trends and patterns that can significantly impact business strategy. For example, analyzing customer demographics linked to policy purchases can reveal specific market segments with high potential. Similarly, analyzing customer interaction data, such as email open rates or website visits, can help tailor marketing campaigns for maximum effectiveness. By tracking customer behavior related to claims, insurers can identify potential fraud patterns or common causes of accidents.
This data can be used to develop targeted prevention programs and refine risk assessment models. Analyzing customer feedback, gathered through surveys or online reviews, reveals areas for service improvement and highlights customer pain points.
Improving Underwriting Decisions with CRM Data
CRM data plays a crucial role in improving underwriting decisions. By analyzing historical claim data linked to specific customer profiles, underwriters can better assess risk. For example, analyzing past claims for similar policyholders can help predict future claim probabilities, enabling more accurate risk scoring. Integrating external data sources, such as credit scores or driving records, further enhances the accuracy of risk assessments.
This allows underwriters to offer more competitive premiums to low-risk customers while appropriately pricing policies for higher-risk individuals. The ultimate goal is to minimize losses while maintaining a fair and competitive pricing structure.
Dashboard Visualizing Key CRM Metrics
A well-designed dashboard provides a quick overview of key CRM metrics for insurance management. The following table illustrates a sample dashboard:
| Metric | Value | Trend | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Policies Sold (Monthly) | 1200 | Up 10% | Good |
| Average Claim Processing Time | 7 days | Down 2 days | Excellent |
| Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) | 4.5/5 | Stable | Good |
| Churn Rate | 5% | Down 1% | Good |
Compliance and Security
Protecting customer data is paramount in the insurance industry. A robust security framework within your CRM system isn’t just a good idea; it’s a legal and ethical necessity. Failing to do so can lead to severe financial penalties, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. This section Artikels best practices for ensuring data security and regulatory compliance within your insurance CRM.Data security and privacy best practices involve a multi-layered approach, encompassing technical safeguards, employee training, and ongoing monitoring.
Effective implementation requires a commitment from all levels of the organization. Ignoring even one aspect can compromise the entire system.
Data Security and Privacy Best Practices
Implementing strong data security measures requires a comprehensive strategy. This includes employing robust access controls, encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest, and regularly updating software and security protocols. Regular security audits and penetration testing identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. Employee training on data security best practices and phishing awareness is crucial to prevent insider threats and social engineering attacks.
A well-defined data retention policy ensures compliance with regulations and minimizes risk. Consider implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts to add an extra layer of security. Regularly backing up data to a secure offsite location protects against data loss due to hardware failure or natural disasters.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements, Insurance customer relationship management
Insurance CRM data management must adhere to a range of regulations, varying by jurisdiction. These regulations often include data privacy laws like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe, CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in California, and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States for health insurance data. Compliance involves understanding the specific requirements of each relevant regulation, implementing appropriate controls, and maintaining comprehensive documentation to demonstrate compliance.
Regular updates to policies and procedures are necessary to keep pace with evolving regulations and best practices. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and legal action. For example, a company found violating GDPR could face fines up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
Data Breach Prevention and Protection
Preventing data breaches requires a proactive and layered approach. This includes implementing robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and anti-malware software. Regular security assessments and penetration testing help identify and address vulnerabilities. Employee training on security awareness is crucial to prevent phishing attacks and other social engineering techniques. Data encryption both in transit and at rest protects sensitive information even if a breach occurs.
Incident response plans should be in place to minimize the impact of a potential breach, including procedures for notification of affected individuals and regulatory authorities. Consider implementing a data loss prevention (DLP) system to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control.
Regular Compliance Audits
Regular audits of the insurance CRM system are essential to ensure ongoing compliance with relevant regulations and security best practices. These audits should assess data security controls, access management, data encryption, and incident response procedures. They should also review compliance with relevant data privacy laws and regulations. Audits should be conducted by independent third-party auditors to ensure objectivity and credibility.
The findings of the audits should be documented and used to improve security and compliance measures. Regular audits demonstrate a commitment to data protection and help mitigate the risk of data breaches and regulatory penalties. The frequency of audits should be determined based on risk assessment and regulatory requirements, but annual audits are generally considered a minimum.
Future Trends in Insurance CRM
The insurance industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven largely by advancements in technology. Customer expectations are rising, and competition is fierce. To thrive, insurers must embrace innovative CRM strategies that leverage the power of emerging technologies to deliver personalized experiences, streamline operations, and gain a competitive edge. This section explores the key future trends shaping the landscape of insurance CRM.
The convergence of data analytics, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing is fundamentally reshaping how insurance companies interact with their customers and manage their operations. This evolution presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges for insurers looking to modernize their CRM systems.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Insurance CRM
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are rapidly changing the game for insurance CRM. AI-powered chatbots provide instant customer support, answering frequently asked questions and resolving simple issues 24/7. ML algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict customer behavior, enabling more accurate risk assessment and personalized product recommendations. For example, an insurer might use ML to identify customers likely to churn and proactively offer them retention incentives.
This proactive approach significantly improves customer retention rates and reduces churn costs. Predictive modeling, powered by AI, also optimizes claims processing by identifying potentially fraudulent claims or speeding up legitimate claim approvals based on pattern recognition.
Challenges and Opportunities in Adopting New CRM Technologies
Adopting new CRM technologies presents both challenges and opportunities. A major challenge is the cost of implementation and integration with existing systems. Upgrading infrastructure, training employees, and ensuring data security can be expensive and time-consuming. However, the opportunities are substantial. Improved customer engagement, increased operational efficiency, and data-driven decision-making can lead to significant cost savings and revenue growth.
For example, a well-implemented AI-powered CRM system can automate many manual tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more complex and strategic activities. The improved customer experience, in turn, leads to increased customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Innovative CRM Applications in the Insurance Industry
Several innovative CRM applications are already transforming the insurance industry. One example is the use of telematics in auto insurance. Telematics devices track driving behavior, providing insurers with data to personalize premiums based on individual risk profiles. This results in fairer pricing and incentivizes safer driving habits. Another example is the use of AI-powered fraud detection systems, which analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns indicative of fraudulent claims, significantly reducing losses due to fraud.
Furthermore, personalized marketing campaigns driven by customer data analytics allow insurers to target specific customer segments with tailored offers, improving conversion rates and boosting sales.
Key Features of a Next-Generation Insurance CRM System
The next generation of insurance CRM systems will need to be highly adaptable and scalable to meet the evolving needs of the industry. Here are some key features:
- AI-powered personalization: Delivering tailored experiences based on individual customer data and preferences.
- Omnichannel integration: Providing seamless customer interactions across all channels (web, mobile, email, phone).
- Advanced analytics and reporting: Generating actionable insights from customer data to improve decision-making.
- Seamless integration with other systems: Connecting CRM with policy administration systems, claims processing systems, and other relevant applications.
- Robust security and compliance features: Protecting sensitive customer data and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
- Predictive modeling capabilities: Forecasting customer behavior and identifying potential risks.
- Self-service portals: Empowering customers to manage their policies and access information independently.
Customer Segmentation and Targeting
Effective customer segmentation is crucial for maximizing the return on investment from your insurance CRM. By grouping customers with similar characteristics, you can tailor your marketing efforts, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately boost sales. This involves leveraging the data within your CRM to identify key patterns and behaviors.
Tailoring marketing campaigns to specific customer segments allows for more personalized and effective communication. Instead of a blanket approach, you can craft messaging that resonates deeply with each group’s unique needs and preferences, leading to higher conversion rates and stronger customer relationships.
Customer Segmentation Methods
Several methods exist for segmenting insurance customers using CRM data. These methods often overlap and can be combined for a more nuanced understanding of your customer base. The goal is to create segments that are both actionable and meaningful for your marketing and sales strategies.
- Demographic Segmentation: This classic approach uses readily available data like age, gender, location, income, and occupation. For example, you might segment customers into “young professionals” or “retired seniors,” each with different insurance needs and preferences.
- Behavioral Segmentation: This method focuses on customer actions and interactions. Examples include claims history (frequency and severity), policy type, online engagement (website visits, email opens), and response to past marketing campaigns. A segment could be “high-risk drivers” or “customers actively seeking quotes online.”
- Psychographic Segmentation: This delves into customer attitudes, values, and lifestyles. While more challenging to obtain directly from CRM data, it can be inferred from other data points. For instance, customers who frequently engage with eco-conscious content might be segmented as “environmentally conscious,” influencing the messaging around green insurance options.
- Policy-Based Segmentation: This straightforward method groups customers based on the type of insurance policies they hold (auto, home, life, etc.) and the coverage levels. This allows for targeted offers related to add-ons or upgrades relevant to their existing policies.
Tailoring Marketing Campaigns
Once segments are defined, crafting targeted campaigns becomes straightforward. For example, a campaign targeting “high-risk drivers” might focus on safety features and driver training discounts, while a campaign aimed at “retired seniors” might emphasize long-term care insurance and simplified claims processes. The key is to personalize the messaging and channel to resonate with each segment’s specific concerns and preferences.
Using CRM, you can easily automate the delivery of these tailored messages through email, direct mail, or in-app notifications.
Tracking Marketing Effectiveness
Your CRM should provide robust tools for tracking the success of your targeted marketing efforts. Key metrics to monitor include:
- Conversion Rates: Track the percentage of customers within each segment who take the desired action (e.g., purchasing a policy, upgrading coverage, renewing their policy).
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculate the cost of acquiring a new customer within each segment to assess the efficiency of your campaigns.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measure the overall profitability of each targeted campaign by comparing the revenue generated against the marketing expenses.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Estimate the total revenue expected from a customer over their relationship with your company. This helps determine the long-term value of your segmentation efforts.
Organizing a Customer Segmentation Strategy
A successful segmentation strategy requires a structured approach. Here’s an example utilizing CRM data points:
This example utilizes a hypothetical insurance company’s CRM data. The values are illustrative and should be adjusted based on your specific data and goals.
- Data Points: Age, Income, Location, Claims History (Frequency, Severity), Policy Type, Online Engagement (Website Visits, Email Opens), Response to Past Marketing Campaigns.
- Segmentation Criteria: Define specific thresholds for each data point to create distinct segments. For instance: Age (Under 30, 30-50, Over 50); Income (Low, Medium, High); Claims History (Low, Medium, High); Online Engagement (High, Low).
- Segment Creation: Combine the criteria to create meaningful segments. For example: “Young, High-Income, Low Claims, High Online Engagement,” or “Older, Medium Income, High Claims, Low Online Engagement.”
- Campaign Personalization: Develop unique marketing messages and channels for each segment. For instance, offer discounts on safety features to high-risk drivers, while promoting long-term care insurance to older customers.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously track key metrics (conversion rates, CAC, ROI, CLTV) to assess the effectiveness of your segmentation and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review and refine your segments to keep them relevant and responsive to changing customer behaviors.
Handling Customer Complaints and Feedback
Effective complaint and feedback management is crucial for building trust and loyalty in the insurance industry. A well-structured process, leveraging CRM capabilities, allows insurers to address customer concerns promptly and transform negative experiences into opportunities for improvement. This proactive approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also provides valuable insights for refining products and services.
A streamlined process for managing customer complaints begins with efficient routing and prioritization within the CRM system. Upon receiving a complaint, whether via phone, email, or online portal, the CRM automatically logs the issue, assigning it to the appropriate department or agent based on pre-defined rules and customer profiles. The system tracks the complaint’s progress, ensuring timely responses and resolution.
Automated notifications keep both the customer and internal teams updated on the status, fostering transparency and minimizing frustration. Regular reporting features within the CRM provide a comprehensive overview of complaint volumes, types, and resolution times, enabling proactive identification of recurring issues and areas needing improvement.
Complaint Management Process Using CRM
The CRM system facilitates a multi-stage complaint handling process. First, complaints are categorized and prioritized based on severity and urgency. Next, an acknowledgement is sent to the customer, assuring them their complaint is being addressed. The assigned agent investigates the issue, gathers relevant information, and updates the CRM system with progress. The agent then proposes a resolution, which is reviewed and approved by a supervisor before being communicated to the customer.
Finally, the complaint is closed, and customer satisfaction is assessed through a follow-up survey or interaction.
Gathering and Analyzing Customer Feedback
CRM systems offer several methods for gathering customer feedback. Surveys can be integrated directly into the CRM, allowing for automated distribution following interactions or policy updates. Feedback forms on the company website or mobile app can be linked to the CRM, ensuring seamless data capture. Social media monitoring tools can be integrated with the CRM to identify and address customer concerns expressed on various platforms.
Analyzing this feedback involves using CRM’s reporting tools to identify trends and patterns. Sentiment analysis can gauge the overall tone of feedback, highlighting areas requiring immediate attention. This data can be segmented by customer demographics, policy type, or other relevant factors for a more granular understanding.
Using Customer Feedback for Product and Service Improvement
Customer feedback is a goldmine of insights for product and service improvement. By analyzing feedback trends, insurers can identify areas needing improvement in their policies, claims processes, or customer service interactions. For example, consistently negative feedback about the claims process might indicate a need for streamlining procedures or improving communication. Feedback on policy features can help identify gaps in coverage or areas where customers find the product confusing or lacking.
This data-driven approach allows for targeted improvements, enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering a competitive advantage.
Turning Negative Feedback into Positive Customer Experiences
Negative feedback should be viewed as an opportunity to improve and build stronger customer relationships. A prompt and empathetic response to a complaint, addressing the customer’s concerns directly and offering a sincere apology, can transform a negative experience into a positive one. Offering compensation, such as a discount on future premiums or expedited service, demonstrates a commitment to customer satisfaction.
Following up with the customer after the issue is resolved to ensure their satisfaction shows that their feedback is valued. By actively addressing negative feedback, insurers can turn detractors into loyal advocates, strengthening their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Conclusive Thoughts
Mastering Insurance Customer Relationship Management isn’t just about adopting new technology; it’s about fundamentally changing how you approach customer interactions. By leveraging CRM’s power to personalize communication, streamline operations, and gain valuable insights, insurance companies can cultivate loyalty, improve efficiency, and ultimately, thrive in a competitive market. The future of insurance CRM lies in embracing innovative technologies like AI and machine learning to further enhance customer experiences and optimize business processes.
This journey into the world of insurance CRM should leave you equipped to leverage its transformative potential.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the biggest challenges in implementing an insurance CRM system?
Common challenges include data migration issues, integrating with existing systems, employee resistance to change, and ensuring data security and compliance.
How can CRM improve customer retention rates?
By personalizing communications, proactively addressing issues, and providing excellent service, CRM fosters customer loyalty and reduces churn.
What is the return on investment (ROI) of an insurance CRM system?
ROI varies, but benefits include increased efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and higher sales conversion rates. Measuring ROI requires tracking key metrics.
How does CRM help with regulatory compliance?
CRM systems help manage customer data securely and transparently, aiding compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA by providing audit trails and facilitating data access requests.
Can CRM be used for cross-selling and upselling insurance products?
Absolutely. CRM provides insights into customer needs and preferences, enabling targeted marketing campaigns to offer relevant products and services.






