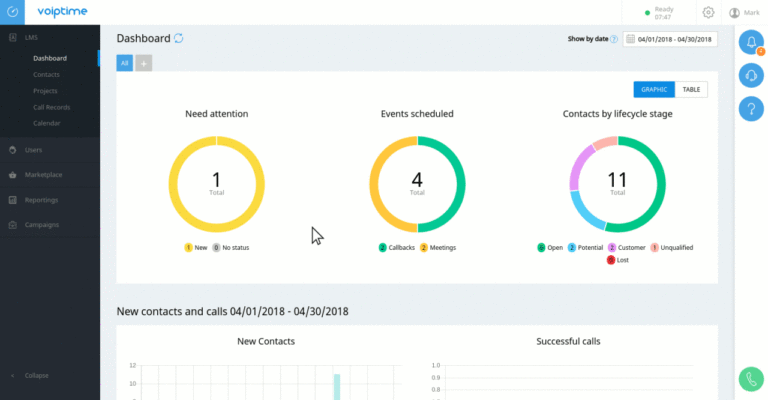
CRM tools for insurance brokers are revolutionizing the industry, transforming how brokers manage clients, track policies, and boost sales. Forget endless spreadsheets and scattered notes; modern CRM systems offer a centralized hub for all your crucial information, empowering you to build stronger client relationships, streamline workflows, and ultimately, increase profitability. This guide dives deep into the world of CRM solutions tailored specifically for the insurance brokerage landscape, exploring various options, key features, and implementation strategies to help you choose the perfect tool for your business.
We’ll explore different CRM types – cloud-based, on-premise, and hybrid – examining their pros and cons in detail. We’ll then delve into essential features like lead management, policy tracking, and reporting, highlighting how these functionalities contribute to efficiency and growth. The guide also covers crucial considerations for selecting a CRM based on your brokerage’s size and specific needs, offering practical advice on implementation, training, and measuring ROI.
Types of CRM Tools for Insurance Brokers
Choosing the right CRM is crucial for insurance brokers to streamline operations, improve client relationships, and boost sales. The market offers a variety of options, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding the different types of CRM deployments – cloud-based, on-premise, and hybrid – is the first step in making an informed decision.
CRM Deployment Types and Their Suitability for Insurance Brokers
The choice between cloud, on-premise, and hybrid CRM solutions depends heavily on the broker’s specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. Each option offers a unique set of advantages and disadvantages.
| Type | Name (Example) | Key Features | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud-Based | Salesforce Sales Cloud, HubSpot CRM | Lead management, contact management, policy tracking, communication tools (email, SMS, phone integration), reporting and analytics, mobile accessibility, integrations with other insurance software. | Subscription-based (monthly or annual fees), often tiered based on features and user numbers. |
| On-Premise | Microsoft Dynamics 365 (on-premise version), some smaller, specialized insurance CRMs | Similar features to cloud-based solutions, but hosted on the broker’s own servers. Greater control over data and security. | One-time license fee, plus ongoing maintenance and support costs. Can be significantly more expensive upfront. |
| Hybrid | Custom solutions combining cloud and on-premise components | Combines the benefits of both cloud and on-premise solutions, allowing brokers to choose which data and functions are hosted where. Offers flexibility. | Varies greatly depending on the specific configuration and chosen components. Typically a combination of subscription and license fees. |
Crucial CRM Features for Insurance Brokers
Regardless of the deployment type, several key features are essential for insurance brokers to maximize efficiency and client satisfaction. These include robust lead management capabilities, comprehensive policy tracking tools, and seamless client communication channels.
Lead Management: Effective lead management involves capturing, nurturing, and converting leads into clients. A good CRM should allow brokers to track lead sources, assign leads to agents, and automate follow-up communications. This ensures no potential client slips through the cracks.
Policy Tracking: Insurance brokers handle numerous policies, and a CRM’s ability to track policy details, renewal dates, and client communication related to each policy is crucial for avoiding lapses and ensuring timely renewals. This feature often includes automated reminders and alerts.
Client Communication: Seamless communication is paramount. A good CRM should integrate with email, SMS, and potentially phone systems, allowing brokers to easily contact clients, schedule appointments, and manage communications effectively. This helps build stronger relationships and improves client retention.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CRM Deployment Types
Cloud-Based CRM: Advantages include lower upfront costs, scalability, accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, and automatic updates. Disadvantages can include reliance on internet connectivity, potential security concerns (though reputable providers have robust security measures), and potential vendor lock-in.
On-Premise CRM: Advantages include greater control over data and security, customization options, and potentially lower ongoing costs (once the initial investment is made). Disadvantages include high upfront costs, significant IT infrastructure requirements, and the need for in-house expertise for maintenance and updates.
Hybrid CRM: Advantages include flexibility, allowing brokers to tailor the solution to their specific needs and security requirements. Disadvantages include higher complexity in setup and management, requiring expertise in both cloud and on-premise technologies. Cost can also be a significant factor depending on the chosen configuration.
Key Features of Effective Insurance Broker CRM Systems
A robust CRM system is no longer a luxury but a necessity for insurance brokers aiming to thrive in today’s competitive landscape. It provides the backbone for efficient operations, improved client relationships, and ultimately, increased profitability. By centralizing client information, automating tasks, and providing insightful analytics, a well-implemented CRM system significantly enhances the overall effectiveness of an insurance brokerage.Effective insurance broker CRM systems offer a suite of features designed to streamline various aspects of the business, from initial client contact to policy renewal.
These features work in concert to improve efficiency, reduce administrative burden, and ultimately, foster stronger client relationships. This leads to better customer retention and increased sales opportunities.
Essential CRM Features for Insurance Brokers
The following table details five essential features that any effective insurance broker CRM should possess. These features directly address common challenges faced by brokers and offer tangible solutions for improved efficiency and productivity.
| Feature Name | Description | Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Client Relationship Management (CRM) | Centralized database storing all client information (contact details, policy information, communication history, etc.). Allows for personalized communication and efficient tracking of client interactions. | Improved client service, reduced administrative time spent searching for information, increased client retention through personalized interactions. | Requires consistent data entry to maintain accuracy. Integration issues may arise if not properly configured with other systems. |
| Sales Pipeline Management | Visual representation of the sales process, tracking leads through various stages (prospecting, qualification, proposal, closing, etc.). Allows for monitoring progress and identifying bottlenecks. | Improved sales forecasting, better lead management, faster sales cycle, increased sales conversion rates. | Requires diligent tracking and updates to maintain accuracy. May require customization to fit specific sales processes. |
| Reporting and Analytics | Provides dashboards and reports on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales conversion rates, client retention, and revenue generation. Offers valuable insights into business performance. | Data-driven decision making, identification of areas for improvement, improved performance tracking, and better resource allocation. | Requires understanding of data interpretation and analysis. Over-reliance on data without considering qualitative factors can be detrimental. |
| Automated Workflows and Tasks | Automates repetitive tasks such as email reminders, follow-ups, and report generation, freeing up time for more strategic activities. | Increased efficiency, reduced administrative burden, improved accuracy, and more time for client interaction and business development. | Initial setup and configuration can be time-consuming. Requires careful planning to avoid errors or unintended consequences. |
| Document Management | Centralized storage and management of all client-related documents (policies, proposals, correspondence, etc.). Ensures easy access and retrieval of information. | Improved organization, reduced risk of losing important documents, faster access to information, and improved compliance. | Requires a robust system with strong security measures to protect sensitive client data. May require training for staff on proper document management practices. |
Integration with Other Business Tools, CRM tools for insurance brokers
Integration with other business tools is crucial for maximizing the value of a CRM system within an insurance brokerage. Seamless data flow between the CRM and other platforms like email marketing software (e.g., Mailchimp, Constant Contact), accounting software (e.g., Xero, QuickBooks), and policy administration systems streamlines operations and eliminates data silos. For instance, automatically updating client information across all platforms after a policy change ensures data consistency and prevents errors.
This integration minimizes manual data entry, reduces the risk of errors, and provides a holistic view of the business. Imagine the efficiency gained by automatically updating client records in your accounting software after a successful policy sale, recorded in your CRM. This integrated approach improves data accuracy and saves significant time.
Selecting the Right CRM for Different Brokerage Sizes
Choosing the right CRM is crucial for insurance brokers, regardless of size. A system that’s perfectly suited for a small brokerage might be completely inadequate for a large enterprise, and vice versa. The ideal CRM should seamlessly integrate with existing workflows, improve efficiency, and ultimately drive growth. This section explores how different CRM solutions cater to the unique needs of small, medium, and large insurance brokerages.
The key to successful CRM implementation lies in understanding your brokerage’s specific requirements. Factors like budget, team size, technological expertise, and the complexity of your sales processes all play a significant role in determining the most appropriate system. A careful assessment of these factors will help you avoid costly mistakes and ensure a smooth transition to a more efficient workflow.
CRM Solutions for Different Brokerage Sizes
This section compares three CRM solutions, each designed to address the specific needs of a different size brokerage. We’ll consider pricing, scalability, and key features to highlight the advantages of choosing the right fit.
- Small Brokerage (1-10 employees): A simple, user-friendly CRM with a focus on contact management and basic reporting is ideal. A cloud-based solution is often preferred due to its low cost and accessibility. Examples include HubSpot CRM (free plan available) or Zoho CRM (affordable starting price). These solutions usually offer basic features such as contact management, task management, and simple reporting, sufficient for smaller operations.
- Medium Brokerage (11-50 employees): Medium-sized brokerages require more robust features, including sales pipeline management, automation capabilities, and more sophisticated reporting tools. They might consider systems like Salesforce Sales Cloud (offers various pricing tiers) or Pipedrive (flexible pricing options). These offer advanced features like lead scoring, sales forecasting, and integration with other business tools, facilitating improved team collaboration and sales tracking.
- Large Brokerage (50+ employees): Large brokerages need highly scalable and customizable CRM solutions capable of handling a large volume of data and integrating with various other systems. They may opt for enterprise-level solutions like Salesforce Sales Cloud (enterprise edition) or Microsoft Dynamics 365 (highly configurable and scalable). These systems often incorporate advanced features like AI-powered insights, complex reporting dashboards, and robust security measures.
Comparison of CRM Solutions
The following table provides a simplified comparison of three example CRM systems, one for each size category. Note that pricing can vary significantly based on the specific features and number of users.
| Feature | HubSpot CRM (Small) | Salesforce Sales Cloud (Medium) | Salesforce Sales Cloud (Enterprise) (Large) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Free plan available, paid plans starting at a low cost | Various pricing tiers, starting at a moderate cost | Enterprise pricing, typically higher cost |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Moderate scalability | Highly scalable |
| Contact Management | Basic | Advanced | Highly advanced, including segmentation and automation |
| Sales Pipeline Management | Basic | Advanced, including lead scoring and forecasting | Highly advanced, including AI-powered insights |
| Reporting & Analytics | Basic | Advanced | Highly advanced, customizable dashboards |
| Integrations | Limited | Extensive | Extensive, including custom integrations |
Factors to Consider When Selecting a CRM
Selecting the right CRM requires a careful consideration of several key factors. Ignoring these factors can lead to a poorly fitting system and wasted resources.
- Budget: Clearly define your budget before you begin your search. CRM systems range from free options to expensive enterprise solutions. Align your choice with your financial capabilities.
- Team Size and Structure: The number of users and the complexity of your sales processes will influence your CRM needs. A smaller team may need a simpler system, while a larger team may require a more complex solution with advanced collaboration tools.
- Technological Expertise: Consider your team’s technological expertise. Some CRMs are more user-friendly than others. Choose a system that your team can easily adopt and use effectively. Extensive training may be required for more complex systems.
CRM Implementation and Training for Insurance Brokers
Successfully implementing a CRM system is crucial for any insurance brokerage looking to streamline operations and improve client relationships. It’s not just about choosing the right software; it’s about a well-planned rollout, thorough training, and ongoing support to ensure user adoption and maximize return on investment. Ignoring these aspects can lead to system underutilization and wasted resources.Implementing a new CRM system requires a strategic approach, moving methodically through key stages to minimize disruption and maximize efficiency.
A well-structured plan, including comprehensive training, is key to achieving a smooth transition and encouraging staff buy-in. This ultimately translates to improved productivity and better client service.
Data Migration Strategies
Data migration is a critical first step. It involves transferring existing client data, policy information, and communication records from your old system (or disparate spreadsheets) into the new CRM. This process needs meticulous planning and execution to avoid data loss or corruption. A phased approach, starting with a small sample data set to test the migration process, is recommended before moving the entire database.
Consider using a reputable data migration specialist if your internal resources are limited or the data volume is extensive. Thorough data cleansing before migration is crucial; cleaning up inconsistencies and inaccuracies beforehand will improve data quality in the new system.
User Training Programs
Comprehensive user training is essential for successful CRM adoption. Training should be tailored to different user roles and skill levels. For example, sales staff might need training on lead management and opportunity tracking, while administrative staff might focus on data entry and reporting. Training methods should be varied and engaging, combining online modules, hands-on workshops, and one-on-one coaching.
Regular refresher training and ongoing support are crucial to address any questions or challenges that arise after the initial implementation. Providing quick reference guides and cheat sheets can help users quickly access information and resolve minor issues independently. Consider using a blended learning approach combining online modules with in-person workshops for optimal learning outcomes.
Ongoing Support and Maintenance
Ongoing support is crucial for long-term success. This includes providing access to helpdesk support, regular system updates, and ongoing training to address new features or changes in the system. Establishing a dedicated support team or partnering with the CRM vendor for ongoing maintenance is essential. Regular system checks for performance issues, data integrity, and security updates are also vital to ensure the smooth functioning of the CRM.
Proactive monitoring and preventative maintenance will minimize downtime and ensure the system remains reliable and efficient.
Addressing Potential Implementation Challenges
Several challenges can arise during CRM implementation. Resistance to change from staff unfamiliar with new technologies is a common hurdle. Addressing this requires clear communication, emphasizing the benefits of the new system and providing adequate training and support. Data integration issues can also occur if the CRM isn’t properly integrated with other systems used by the brokerage.
Careful planning and testing are crucial to avoid such problems. Another potential issue is the lack of management buy-in, leading to insufficient resource allocation for implementation and training. Securing executive sponsorship and demonstrating a clear ROI for the CRM investment can help overcome this challenge. Finally, choosing the wrong CRM for the brokerage’s specific needs can lead to underutilization and ultimately failure.
Careful selection, considering the brokerage’s size, operations, and future growth plans, is crucial.
Improving Client Relationships with CRM Tools
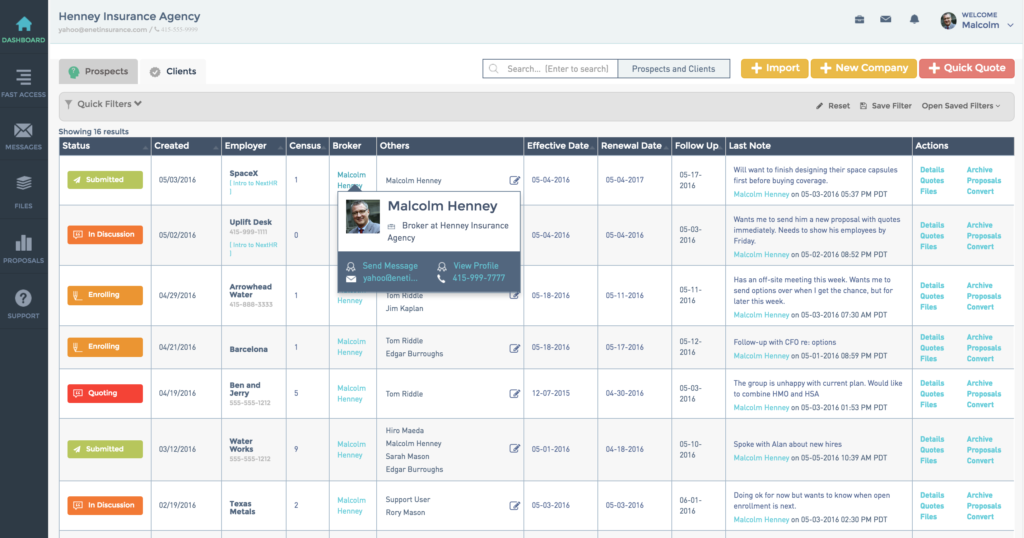
A well-implemented CRM system is more than just a database; it’s a powerful tool for fostering stronger, more profitable relationships with your insurance clients. By leveraging the data captured within the system, brokers can personalize interactions, anticipate client needs, and ultimately boost customer satisfaction and loyalty. This leads to increased retention rates and improved cross-selling opportunities.Effective use of a CRM system allows insurance brokers to move beyond transactional interactions and cultivate genuine, long-lasting relationships with their clients.
This proactive approach not only improves customer satisfaction but also strengthens the broker’s position in a competitive market. The ability to personalize communications and provide timely, relevant support is key to building trust and demonstrating value.
Personalized Client Interactions and Improved Customer Satisfaction
CRM systems provide a centralized repository of client information, including policy details, communication history, and personal preferences. This rich data allows brokers to personalize interactions in several ways. For example, birthday emails with a personalized discount offer or a proactive call to discuss policy renewal approaching its anniversary can significantly enhance the client experience. By understanding individual client needs and preferences, brokers can tailor their communication and service to create a more positive and rewarding relationship.
Analyzing data on past interactions can reveal patterns that inform future communication strategies, ensuring each interaction is relevant and valued by the client. This data-driven approach helps create a more seamless and satisfying client experience, leading to increased loyalty and referrals.
Tracking Client Interactions, Managing Communication, and Identifying Sales Opportunities
A CRM system acts as a central hub for all client interactions. Every phone call, email, and meeting is logged, providing a complete history of the relationship. This detailed record allows brokers to track the effectiveness of their communication strategies and identify areas for improvement. Furthermore, the CRM can be used to automate routine tasks such as sending policy renewal reminders or following up after a client inquiry.
This frees up brokers’ time to focus on building relationships and identifying opportunities for cross-selling and upselling. For instance, if a client recently purchased auto insurance, the CRM might flag them as a potential candidate for homeowners insurance, allowing the broker to proactively reach out and offer a relevant product. The system’s ability to analyze client data and identify these opportunities is crucial for driving revenue growth.
Effective Client Communication Strategies Facilitated by CRM Tools
Automated email sequences are a highly effective tool for nurturing leads and maintaining client relationships. A series of automated emails can be triggered based on specific events, such as a policy purchase or a service inquiry. These emails can provide valuable information, answer common questions, and reinforce the broker’s commitment to client service. Personalized follow-ups are also crucial.
After a client meeting or phone call, the CRM can automatically generate a follow-up email summarizing the key discussion points and next steps. This ensures that no detail is overlooked and reinforces the broker’s attention to detail. For example, a broker could set up an automated sequence for new clients, providing welcome information, policy details, and contact information in a series of emails over the first month.
Another example would be a sequence of emails leading up to policy renewal, reminding the client of the upcoming date and offering opportunities to review coverage or make adjustments. These automated sequences, coupled with personalized follow-ups, demonstrate a commitment to client service and build strong, lasting relationships.
Measuring the ROI of CRM Systems in Insurance Brokerages
Implementing a CRM system represents a significant investment for any insurance brokerage. Understanding and demonstrating its return on investment (ROI) is crucial for justifying the expense and securing continued support. This section Artikels key performance indicators (KPIs) and methods for tracking and analyzing data to showcase the value of your CRM.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Measuring CRM Effectiveness
Effective measurement requires focusing on relevant metrics that directly reflect the impact of the CRM system. These KPIs should align with the brokerage’s overall business goals and provide a clear picture of the system’s contribution to success.
- Increased Sales Revenue: Track the revenue generated from leads and sales opportunities managed within the CRM. Compare this to pre-CRM sales figures to demonstrate the increase attributable to improved lead management and sales processes.
- Improved Customer Retention Rate: Monitor the percentage of clients retained over a specific period. A CRM system facilitates better client communication and personalized service, leading to higher retention rates. Analyze churn rates before and after CRM implementation to quantify the improvement.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Calculate the reduction in costs associated with manual tasks previously performed. Examples include reduced administrative time spent on data entry, improved efficiency in communication, and minimized errors related to policy management.
- Enhanced Lead Conversion Rate: Measure the percentage of leads that convert into paying customers. A CRM system allows for better lead qualification and targeted follow-up, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
- Increased Policy Sales per Client: Analyze the average number of policies sold per client. Effective CRM usage can help upsell and cross-sell additional products, boosting this metric.
- Shorter Sales Cycles: Track the time it takes from initial lead contact to policy sale. CRM streamlines communication and reduces delays, resulting in shorter sales cycles.
Tracking and Analyzing CRM Data for ROI Demonstration
Data analysis is the key to showcasing the ROI. The CRM system itself should provide reporting capabilities, allowing you to extract the necessary data. However, you might need to supplement this with data from other sources, such as your accounting software.
Regularly scheduled reports (e.g., monthly or quarterly) should be generated to track the KPIs mentioned above. These reports should compare performance before and after CRM implementation, highlighting the positive changes. It’s also important to segment data (e.g., by sales team, product line, or client segment) to identify areas of strength and weakness.
Sample ROI Report
| Metric | Before CRM Implementation | After CRM Implementation | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Sales Revenue | $1,000,000 | $1,250,000 | +25% |
| Customer Retention Rate | 80% | 88% | +8% |
| Operational Costs (Administrative) | $50,000 | $40,000 | -20% |
| Lead Conversion Rate | 10% | 15% | +5% |
Note: This is a simplified example. A real-world report would include more detailed data and analysis, potentially incorporating a cost-benefit analysis to quantify the overall ROI more precisely. For example, calculating the return on the initial investment in the CRM software and associated training costs should be included.
Last Recap: CRM Tools For Insurance Brokers
Ultimately, selecting and implementing the right CRM is a strategic investment that can significantly impact your insurance brokerage’s success. By carefully considering your specific needs, exploring available options, and planning a robust implementation strategy, you can harness the power of CRM to enhance client relationships, optimize operations, and drive significant growth. Remember, a well-chosen CRM isn’t just a software; it’s a powerful tool for building a more efficient, profitable, and client-focused brokerage.
Don’t hesitate to leverage the insights gained here to propel your business forward.
Expert Answers
What is the average cost of a CRM for insurance brokers?
Costs vary wildly depending on features, vendor, and the number of users. Expect to pay anywhere from a few hundred dollars per month for basic cloud-based solutions to thousands for enterprise-level systems with extensive customization.
How long does it typically take to implement a new CRM system?
Implementation time depends on the complexity of the system and the size of your brokerage. Simple cloud-based systems might be up and running within weeks, while more complex deployments could take several months.
What if my brokerage uses multiple insurance platforms? Can the CRM integrate with them?
Many CRMs offer integrations with various insurance platforms. Check the CRM’s compatibility before committing to a purchase. If your preferred platforms aren’t supported, consider a CRM with robust API capabilities for custom integrations.
Can a CRM help me comply with insurance regulations?
While a CRM won’t directly ensure compliance, it can assist by providing tools to track client data, communications, and policy details, making audits easier and helping maintain accurate records, which is crucial for regulatory compliance.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when choosing a CRM?
Common mistakes include focusing solely on price without considering features, failing to adequately assess your brokerage’s needs, and neglecting proper training and ongoing support for your team.