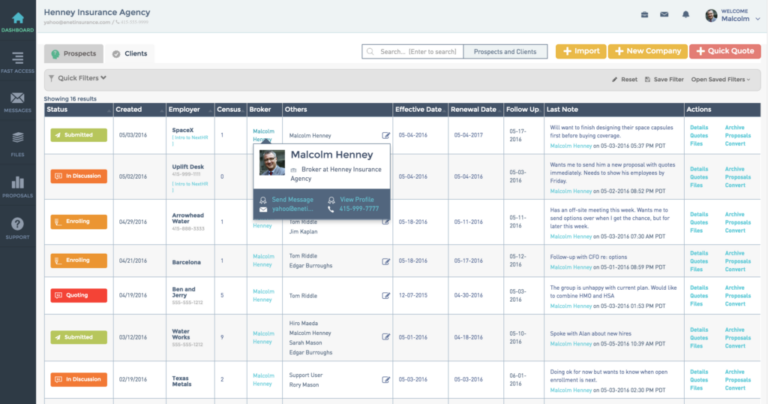
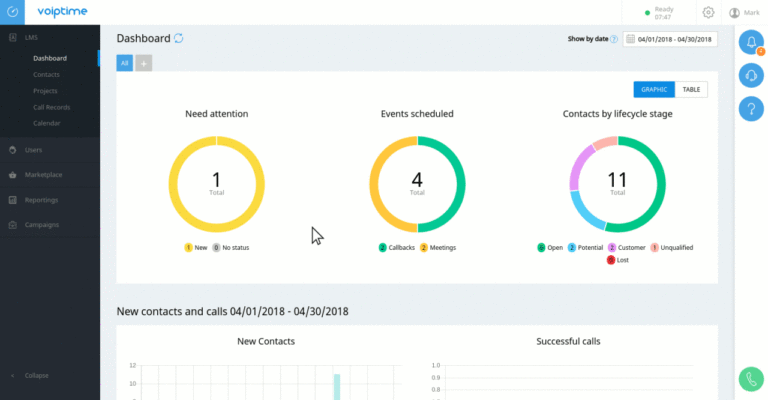
Top insurance CRM systems are revolutionizing how insurance companies manage client relationships and streamline operations. Finding the right system is crucial for boosting efficiency, improving customer satisfaction, and ultimately, driving profitability. This guide dives deep into the key features, implementation considerations, and future trends shaping this critical sector of the insurance industry.
From managing policies and claims to generating insightful reports and ensuring regulatory compliance, the selection and implementation of a top-tier CRM system is a strategic decision with far-reaching consequences. We’ll explore the nuances of different systems, helping you navigate the complexities and make an informed choice for your specific needs.
Defining “Top” Insurance CRM Systems: Top Insurance CRM Systems
Picking the right Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is crucial for any insurance agency, regardless of size or specialization. A top-tier system streamlines operations, improves client relationships, and ultimately boosts the bottom line. But what exactly constitutes a “top” insurance CRM? It’s not just about flashy features; it’s about a perfect blend of functionality, ease of use, and scalability tailored to the specific needs of the insurance industry.Defining a “top” insurance CRM system involves considering several key criteria.
These go beyond basic contact management and encompass features specifically designed to address the unique challenges and opportunities within the insurance sector. The ideal system will seamlessly integrate with existing workflows, enhance productivity, and provide valuable insights for better decision-making.
Key Criteria for Top Insurance CRMs
Several factors contribute to a CRM’s ranking as “top.” These include robust contact and policy management capabilities, seamless integration with other business tools, comprehensive reporting and analytics, and a user-friendly interface that promotes adoption across the organization. Furthermore, scalability is paramount; the system should be able to adapt to the company’s growth without requiring significant changes or additional investments.
Finally, strong security features are essential to protect sensitive client data.
CRM Needs Vary Across Insurance Types
The insurance landscape is diverse, encompassing life, health, auto, home, commercial, and many specialized lines. Each type has unique requirements, impacting the features a CRM should prioritize. For instance, a life insurance CRM needs strong lead tracking and follow-up tools to manage long sales cycles, while an auto insurance CRM might focus on efficient claims processing and quick policy renewals.
Health insurance CRMs often need to handle complex medical coding and billing information, requiring more robust integration with healthcare systems. A commercial insurance CRM might prioritize managing large accounts and complex policy structures. Therefore, the “top” CRM will differ depending on the specific insurance lines offered.
Features Differentiating Top-Performing Systems
Top-performing insurance CRMs often include advanced features not found in basic systems. These can include AI-powered lead scoring and predictive analytics to identify high-potential prospects, automated workflows to streamline repetitive tasks like policy renewals and claims processing, and sophisticated reporting dashboards to provide real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs). Integration with external data sources, such as credit bureaus or medical records databases (where applicable and compliant with regulations), is another key differentiator, providing a more comprehensive view of the client.
Furthermore, mobile accessibility and robust customer support are crucial for ensuring widespread adoption and minimizing disruption. For example, a system with automated email sequences for follow-ups and policy reminders significantly improves efficiency compared to manual processes. Similarly, a system with built-in compliance features ensures adherence to industry regulations and reduces the risk of penalties.
Key Features of Leading Insurance CRM Systems
A robust insurance CRM system is far more than just a contact list; it’s the central nervous system of an insurance agency, streamlining operations and improving client relationships. These systems offer a range of features designed to manage every aspect of the insurance lifecycle, from initial contact to claims resolution. Choosing the right system depends on the specific needs of your business, but understanding the core functionalities is crucial.
Leading insurance CRMs offer a powerful blend of contact management, policy management, and claims processing capabilities, all supported by robust reporting and analytics. Seamless integration with other vital insurance software is also a key differentiator. This allows for a truly unified and efficient workflow, eliminating data silos and manual data entry.
Core Functionalities of Robust Insurance CRMs
The core functionality of a leading insurance CRM revolves around three key areas: contact management, policy management, and claims processing. Effective contact management goes beyond simply storing contact information; it involves tracking interactions, managing communication preferences, and segmenting clients for targeted marketing. Policy management encompasses the entire policy lifecycle, from initial quote generation to renewal and cancellation. Claims processing streamlines the submission, review, and settlement of claims, minimizing processing time and improving customer satisfaction.
Reporting and Analytics Capabilities
Effective reporting and analytics are crucial for informed decision-making within an insurance agency. Top-tier systems offer customizable dashboards and reports, providing real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales conversion rates, policy renewal rates, and claims processing times. These systems often incorporate advanced analytics features, such as predictive modeling, to forecast future trends and identify potential risks.
For example, a system might analyze historical claims data to predict future claim costs, allowing for more accurate pricing and risk management.
Different systems vary in their reporting capabilities. Some may offer basic reporting features, while others provide more advanced analytics and predictive modeling. The choice depends on the complexity of your business needs and the level of insight you require.
Integration Capabilities with Other Insurance Software
Seamless integration with other insurance-related software is essential for maximizing efficiency and minimizing data entry. Top insurance CRMs integrate with various systems, including accounting software (e.g., Xero, QuickBooks), billing systems, and policy administration systems. This integration allows for automated data transfer, reducing manual effort and the risk of errors. For example, integrating with an accounting system can automate the recording of payments and commissions, while integration with a policy administration system can streamline the policy lifecycle.
Comparison of Leading Insurance CRM Systems
The following table compares four leading insurance CRM systems based on their policy management, reporting, and integration capabilities. Note that specific features and pricing can vary depending on the chosen plan and the vendor.
| Feature | System A | System B | System C | System D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policy Management | Comprehensive, including quoting, issuance, and renewal | Robust policy management with automated workflows | Strong policy management, but lacks some advanced features | Basic policy management; requires integration with other systems |
| Reporting & Analytics | Customizable dashboards and advanced analytics | Good reporting features, but limited advanced analytics | Basic reporting; limited customization | Limited reporting capabilities |
| Integration Capabilities | Integrates with major accounting and billing systems | Integrates with selected accounting and billing systems | Limited integration capabilities | Minimal integration capabilities |
User Experience and Interface Design
A top-tier insurance CRM isn’t just about powerful features; it’s about how easily agents and staff can access and utilize those features. A user-friendly interface dramatically impacts productivity, reduces errors, and ultimately improves customer satisfaction. A poorly designed system, however, can lead to frustration, wasted time, and a negative impact on the bottom line. Therefore, a focus on intuitive navigation and a clean, efficient design is paramount.The importance of a user-friendly and intuitive navigation system in an insurance CRM cannot be overstated.
Agents spend hours daily interacting with the system; a streamlined experience minimizes time spent searching for information or navigating complex menus. This translates directly into increased efficiency, allowing agents to focus on building relationships with clients and closing deals rather than wrestling with the software. Intuitive design also reduces training time and associated costs, a significant advantage for insurance companies.
Furthermore, a pleasant user experience contributes to higher employee morale and retention.
Effective UI/UX Design Elements in Top-Rated Insurance CRMs
Effective UI/UX design in leading insurance CRMs often incorporates several key elements. These systems typically prioritize clear visual hierarchy, using size, color, and contrast to guide the user’s eye to important information. They also leverage consistent design patterns and intuitive icons to ensure predictability and ease of navigation. For example, a well-designed system might use color-coding to distinguish policy status (e.g., green for active, red for cancelled), making it instantly clear where attention is needed.
Furthermore, customizable dashboards provide agents with a personalized view of their most important tasks and metrics, eliminating the need to sift through irrelevant data. Data visualization tools, such as charts and graphs, are frequently employed to present complex information in an easily digestible format. Finally, robust search functionality allows agents to quickly locate specific clients or policies, saving valuable time.
User Flow Diagram: Policy Creation Process
The following describes a typical policy creation process within a well-designed insurance CRM. Imagine a visual representation, similar to a flowchart, guiding the user through each step.The process begins with the agent selecting “New Policy” from the main dashboard. This opens a form pre-populated with client details if the client already exists in the system. If not, the agent will need to input the client’s information, which is then automatically validated against internal databases and external sources (e.g., for address verification).
Once client details are confirmed, the agent selects the appropriate policy type and enters relevant details such as coverage amounts, deductibles, and payment information. The system then automatically calculates premiums and generates a policy document. The agent reviews the document, makes any necessary corrections, and then submits the policy for approval. Upon approval, the policy is issued, and the system automatically updates the client’s record and sends notifications to relevant parties.
The entire process is designed to be smooth, efficient, and error-free, with clear visual cues guiding the agent at each stage. This seamless flow is a hallmark of a well-designed insurance CRM.
Security and Compliance in Insurance CRM Systems
Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount in the insurance industry. Insurance CRM systems, holding a wealth of personal and financial information, require robust security measures to maintain client trust and comply with stringent regulations. Failure to do so can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. This section details the critical security and compliance aspects of top-tier insurance CRM systems.
Data Encryption and Access Control
Data encryption is fundamental. All data at rest and in transit should be encrypted using strong, industry-standard encryption algorithms like AES-256. Access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), are crucial. RBAC ensures that only authorized personnel have access to specific data, limiting the potential impact of a security breach. For example, a claims adjuster might have access to claim details but not to policyholder financial information.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be mandatory for all users, adding an extra layer of security beyond passwords. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Top insurance CRM systems must adhere to a range of regulations depending on the geographic location and the type of data processed. HIPAA in the US governs the protection of Protected Health Information (PHI), while GDPR in Europe dictates the handling of personal data. Other relevant regulations might include CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) or similar state-level laws.
Compliance involves implementing data privacy controls, providing data subject access requests, and demonstrating accountability through detailed audit trails. Failure to comply can lead to hefty fines and legal action. For instance, a company failing to meet GDPR requirements could face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover.
Best Practices for Maintaining Data Security and Compliance
Maintaining data security and compliance is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. Several best practices are essential:
Regularly update the CRM system’s software and security patches to address known vulnerabilities. Implement a comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) strategy to prevent sensitive data from leaving the controlled environment. Conduct regular employee training on data security best practices and compliance requirements. Maintain detailed audit logs of all system access and data modifications to facilitate investigations and demonstrate compliance.
Establish a robust incident response plan to handle security breaches effectively and minimize their impact. Regularly review and update security policies and procedures to adapt to evolving threats and regulatory changes. Finally, consider employing a third-party security auditor to perform independent assessments and provide recommendations for improvement.
Cost and Implementation Considerations
Choosing the right insurance CRM involves a careful assessment of not just features and functionality, but also the significant financial implications. The total cost of ownership (TCO) can vary dramatically depending on the system, your business size, and your specific needs. Understanding the various cost factors and comparing different pricing models is crucial for making an informed decision.Implementing a new CRM system is a considerable investment, impacting both your immediate budget and long-term operational costs.
Factors like initial licensing fees, customization costs, training expenses, data migration, and ongoing maintenance all contribute to the overall TCO. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is essential to ensure the chosen system delivers a strong return on investment (ROI).
Pricing Models of Leading Insurance CRM Systems
Insurance CRM systems typically employ a few common pricing models. Subscription-based models are prevalent, offering varying tiers with different feature sets and user limits. These often involve monthly or annual payments, providing predictable budgeting. Some vendors may also offer one-time purchase options, though these often lack the ongoing support and updates included in subscription models. Finally, some systems might utilize a per-user, per-month pricing structure, making the cost directly scalable with the size of your team.
The choice depends heavily on your budget, expected growth, and preference for flexibility versus upfront cost.
Factors Affecting Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Estimating the TCO for an insurance CRM requires considering several factors beyond the initial purchase price. These include:
- Software licensing fees: This is the initial cost of acquiring the software, which can vary significantly depending on the system and the number of users.
- Implementation costs: This encompasses professional services for setup, configuration, data migration, and customization, which can be substantial for complex integrations.
- Training costs: Training your staff to effectively use the new system is crucial for maximizing ROI and requires investment in time and resources.
- Ongoing maintenance and support fees: Most subscription-based systems include maintenance and support, but the cost can vary. One-time purchases typically require separate contracts for support.
- Hardware and infrastructure costs: Depending on the system’s requirements, you might need to invest in new hardware or cloud infrastructure to support the CRM.
- Integration costs: Connecting the CRM with existing systems (like your accounting software or policy management system) can incur additional costs.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Example Comparison
Let’s compare two hypothetical systems: System A and System B.
| Factor | System A (Subscription) | System B (One-Time Purchase) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | $5,000 (first year subscription for 10 users) | $20,000 |
| Annual Maintenance | $4,000 | $2,000 (estimated, may increase significantly over time) |
| Implementation Costs | $10,000 | $15,000 |
| Estimated ROI (over 5 years, based on improved efficiency and sales) | $50,000 | $40,000 |
System A, while having higher initial and ongoing costs, offers a higher projected ROI over five years due to included support and updates, leading to greater efficiency and potentially higher sales. System B, with its lower initial cost, carries a higher risk due to potential escalating maintenance costs and lack of guaranteed updates. The best choice depends on your specific circumstances and risk tolerance.
This example illustrates the need for a thorough cost-benefit analysis before committing to a CRM system. Remember that these are hypothetical figures; actual costs will vary based on your specific needs and the vendor’s pricing.
Case Studies of Successful Insurance CRM Implementations
Successfully implementing a CRM system in the insurance industry can significantly boost efficiency and customer satisfaction. However, the journey isn’t always smooth. This section examines real-world examples, highlighting both the triumphs and challenges encountered during implementation and the resulting improvements.
Progressive Insurance’s CRM Transformation
Progressive, a major US auto insurer, leveraged a CRM system to enhance its customer service and operational efficiency. Their implementation involved integrating various data sources to create a single, unified view of the customer. A key challenge was data migration and cleansing – ensuring data accuracy and consistency across different systems. This was addressed through a phased approach, prioritizing critical data points initially and then progressively incorporating more comprehensive data sets.
The result? Improved response times to customer inquiries, a streamlined claims process, and increased customer retention rates, demonstrably improving their bottom line. Their investment in training and change management also played a crucial role in the successful adoption of the new system by their employees.
Allstate’s Enhanced Customer Engagement, Top insurance CRM systems
Allstate, another leading US insurer, focused on improving customer engagement through its CRM implementation. The initial challenge was integrating the CRM with their existing legacy systems, a common hurdle for established organizations. This was tackled through careful planning and the development of robust APIs to ensure seamless data flow. The implementation involved a significant investment in employee training to ensure proper usage and adoption.
The outcome was a more personalized customer experience, increased cross-selling opportunities, and improved customer satisfaction scores, as evidenced by increased positive feedback and higher customer lifetime value.
Farmers Insurance’s Agent Empowerment
Farmers Insurance aimed to empower its agents through a CRM implementation that provided them with a centralized platform for managing customer interactions and sales processes. One of the major challenges was ensuring data security and compliance, given the sensitive nature of customer information. This was addressed by investing heavily in robust security measures and adhering to strict data privacy regulations.
The result was improved agent productivity, increased sales conversions, and enhanced customer loyalty. The improved data accessibility also enabled better targeted marketing campaigns, leading to a higher return on investment for their marketing efforts. The company also saw improvements in agent retention rates due to the increased efficiency and ease of use provided by the CRM.
Future Trends in Insurance CRM Technology

The insurance industry is undergoing a rapid digital transformation, and CRM systems are at the forefront of this change. Emerging technologies are fundamentally altering how insurers interact with customers, manage policies, and assess risk. This evolution promises greater efficiency, personalized service, and improved customer satisfaction.The integration of advanced technologies is driving significant advancements in insurance CRM capabilities, leading to more sophisticated systems capable of handling complex data and providing insightful analytics.
This shift necessitates a proactive approach to understanding and adopting these emerging trends to remain competitive.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Insurance CRMs
AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize insurance CRM. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict customer behavior, enabling proactive risk assessment and personalized offers. For example, an insurer could use machine learning to identify customers likely to renew their policies and offer them tailored discounts or bundled services.
This predictive capability improves customer retention and streamlines operations. Furthermore, AI can automate tasks such as data entry and policy processing, significantly increasing efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Enhanced Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling
Modern insurance CRM systems are increasingly incorporating advanced analytics capabilities. These systems can process and analyze large volumes of data from various sources, including customer interactions, policy information, and external data sources, to provide valuable insights into customer behavior, risk assessment, and fraud detection. Predictive modeling, powered by machine learning, allows insurers to anticipate future events, such as potential claims or policy lapses, enabling proactive interventions and improved risk management.
Imagine a system that identifies customers at high risk of canceling their policy and triggers automated outreach campaigns offering personalized incentives to retain them.
Improved Customer Experience through Personalization
Personalized customer experiences are becoming increasingly crucial in the insurance industry. Advanced CRM systems leverage data analytics and AI to tailor interactions and offerings to individual customer needs and preferences. This might involve providing personalized recommendations for insurance products, offering customized communication channels, or delivering targeted marketing campaigns. For instance, a CRM system could analyze a customer’s driving history and offer them a discounted rate on their auto insurance if they demonstrate safe driving behavior.
Such personalized approaches enhance customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Potential Future Features for Insurance CRMs
The integration of these technologies will likely lead to several new features in future insurance CRM systems. These advancements will significantly enhance operational efficiency and customer experience.
- Hyper-personalized recommendations: CRMs will leverage AI to provide highly tailored insurance product recommendations based on individual customer profiles and real-time data.
- Predictive claims management: Systems will use AI to predict potential claims and proactively address risk factors, reducing claim costs and improving response times.
- Automated underwriting: AI-powered systems will automate parts of the underwriting process, reducing processing times and improving efficiency.
- Enhanced fraud detection: Advanced analytics and machine learning will enhance the detection and prevention of fraudulent claims and activities.
- Seamless omnichannel integration: CRMs will provide a unified view of customer interactions across all channels (web, mobile, phone, email), ensuring consistent and personalized service.
- Blockchain integration for secure data management: Blockchain technology can enhance data security and transparency in insurance transactions and policy management.
Wrap-Up
Choosing the right insurance CRM system is a significant investment, impacting efficiency, customer relationships, and bottom-line results. By carefully considering the features, security protocols, costs, and future-proofing capabilities discussed in this guide, insurance companies can confidently select a system that aligns with their business goals and paves the way for sustained growth and success. Remember, the best system isn’t just about features; it’s about seamless integration into your existing workflows and a user experience that empowers your team.
Questions and Answers
What are the common integration challenges with insurance CRM systems?
Common challenges include data migration issues, API compatibility problems, and the need for custom integrations to connect with legacy systems. Proper planning and selection of a system with robust integration capabilities are key to mitigating these issues.
How do I measure the ROI of an insurance CRM system?
Measure ROI by tracking improvements in key metrics such as reduced operational costs (e.g., lower claim processing times), increased sales conversion rates, improved customer retention, and enhanced agent productivity. Compare these metrics before and after implementation.
What is the typical implementation timeline for an insurance CRM?
Implementation timelines vary depending on the system’s complexity, data migration needs, and the size of the insurance company. Expect a timeline ranging from several weeks to several months.
What training is typically needed for insurance CRM users?
Training needs depend on the system’s complexity and user roles. Expect training to cover core functionalities, reporting features, and data management practices. Effective training minimizes user errors and maximizes system adoption.
Are cloud-based insurance CRMs more secure than on-premise systems?
Cloud-based systems can offer robust security features if chosen from reputable providers who adhere to industry best practices. However, both cloud and on-premise systems require careful security management and compliance with relevant regulations.