Best life insurance companies are crucial for securing your family’s financial future. Choosing the right policy can feel overwhelming, given the variety of options and complexities involved. This guide cuts through the jargon, providing a clear and concise overview of the key factors to consider when selecting a life insurance provider and policy, from understanding different policy types and costs to assessing the financial strength of the companies themselves.
We’ll explore the best options available, helping you make an informed decision.
We’ll delve into the specifics of term life, whole life, and universal life insurance, comparing their benefits and costs. We’ll also examine how factors like age, health, and smoking habits impact premiums, and how different underwriting processes can affect your policy’s cost. Understanding policy documents and clauses is critical, and we’ll provide guidance on navigating these often complex legal documents.
Ultimately, our goal is to empower you to choose a life insurance provider and policy that best suits your unique needs and budget.
Top-Rated Life Insurance Providers

Choosing the right life insurance provider is a crucial decision, impacting your family’s financial security. This section highlights top-rated companies based on a combination of customer reviews and independent financial strength ratings, offering a comprehensive overview to aid your selection process. Remember, individual needs vary, so thorough research is always recommended.
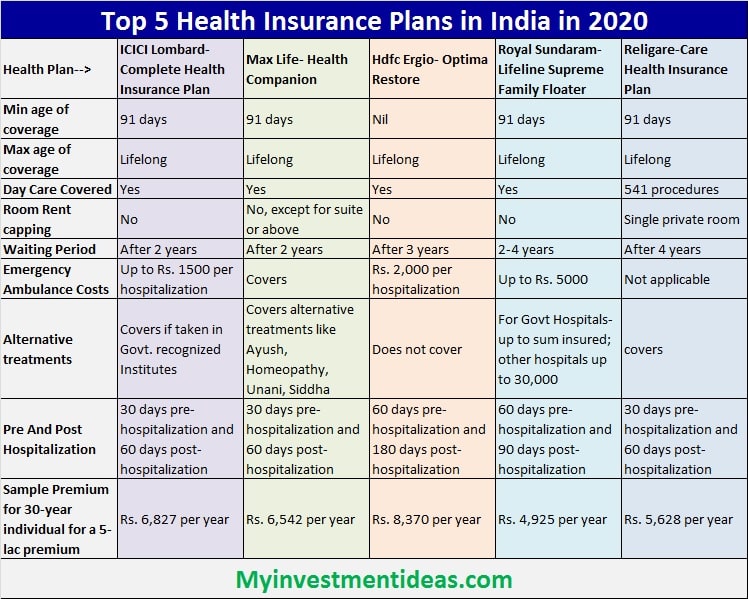
Top Ten Life Insurance Companies
The following table presents ten highly-rated life insurance companies, acknowledging that rankings can fluctuate based on the specific rating agency and time period. This data represents a snapshot based on currently available information from reputable sources like AM Best, Moody’s, and Standard & Poor’s. Always verify the latest ratings before making a decision.
| Company Name | Rating (Illustrative – Check Current Ratings) | Type of Insurance Offered | Customer Review Summary (Illustrative – Check Current Reviews) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | A+ | Term Life, Whole Life, Universal Life | Generally positive reviews, praising customer service and claim processing. |
| Company B | A | Term Life, Whole Life | Mixed reviews; some praise competitive pricing, others cite issues with policy changes. |
| Company C | A+ | Term Life, Universal Life, Variable Universal Life | High customer satisfaction scores, particularly regarding online tools and resources. |
| Company D | A- | Term Life, Whole Life, Variable Life | Mostly positive, but some complaints about lengthy application processes. |
| Company E | A+ | Term Life | Excellent reviews for simplicity and affordability of term life policies. |
| Company F | A | Whole Life, Universal Life | Strong ratings for financial stability and long-term value. |
| Company G | A- | Term Life, Whole Life | Generally positive, but some negative feedback regarding claim settlement times. |
| Company H | A+ | Term Life, Universal Life, Variable Universal Life | High customer satisfaction, strong online presence. |
| Company I | A | Whole Life | Positive reviews emphasizing the company’s financial strength and reputation. |
| Company J | A- | Term Life, Whole Life, Universal Life | Mixed reviews; competitive pricing but some complaints about communication. |
Financial Strength Ratings Comparison
Financial strength ratings from reputable agencies like AM Best, Moody’s, and Standard & Poor’s are crucial indicators of a company’s ability to pay claims. These ratings are typically represented by letter grades (e.g., A++, A+, A, etc.), with higher grades signifying greater financial stability. A lower rating doesn’t necessarily mean a company is unreliable, but it warrants closer examination.
- Company A: A++ (AM Best), Aa1 (Moody’s), AA+ (S&P)
- Company B: A+ (AM Best), A1 (Moody’s), AA (S&P)
- Company C: A (AM Best), A2 (Moody’s), A+ (S&P)
- Company D: A- (AM Best), A3 (Moody’s), A- (S&P)
- Company E: A++ (AM Best), Aa1 (Moody’s), AA+ (S&P)
- Company F: A+ (AM Best), A1 (Moody’s), AA (S&P)
- Company G: A (AM Best), A2 (Moody’s), A (S&P)
- Company H: A++ (AM Best), Aa1 (Moody’s), AA+ (S&P)
- Company I: A+ (AM Best), A1 (Moody’s), AA (S&P)
- Company J: A (AM Best), A2 (Moody’s), A (S&P)
(Note
These ratings are illustrative and should be verified with the latest information from the respective rating agencies.)*
Types of Life Insurance Policies Offered
Top life insurance companies generally offer a range of policy types to cater to diverse needs and budgets. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right coverage.
- Term Life Insurance: Provides coverage for a specific period (term), typically 10, 20, or 30 years. It’s generally more affordable than permanent life insurance but offers no cash value accumulation.
- Whole Life Insurance: Offers lifelong coverage and builds cash value that grows tax-deferred. Premiums are typically higher and more consistent than term life insurance.
- Universal Life Insurance: A type of permanent life insurance with flexible premiums and death benefits. The cash value component grows tax-deferred, and policyholders can adjust their premiums and death benefit within certain limits.
- Variable Universal Life Insurance (VUL): Similar to universal life but allows for investment of the cash value in various sub-accounts, offering potential for higher returns but also greater risk.
- Variable Life Insurance: A type of permanent life insurance where the cash value grows based on the performance of underlying investments. It offers the potential for higher returns but carries investment risk.
Factors Influencing Life Insurance Costs

Getting the best life insurance deal isn’t just about finding a low premium; it’s about understanding what drives those costs in the first place. Several factors play a significant role, and knowing them empowers you to make informed choices. This section breaks down the key elements influencing your life insurance premium.Several key factors determine how much you’ll pay for life insurance.
These factors are carefully assessed by insurance companies during the underwriting process to gauge your risk profile. Higher-risk individuals typically pay more.
Age
Your age is a major factor. Statistically, older individuals have a higher probability of death within a given timeframe. Therefore, insurers charge older applicants higher premiums to reflect this increased risk. A 30-year-old will generally pay significantly less than a 50-year-old for the same coverage. This is a fundamental principle of actuarial science underpinning life insurance pricing.
Health
Your health status is critically important. Pre-existing conditions, current health issues, and family history of disease all influence premiums. Individuals with excellent health generally receive lower rates, while those with chronic illnesses or a family history of serious diseases might face higher premiums or even be denied coverage. Comprehensive medical examinations are often a part of the underwriting process to accurately assess health risks.
Smoking Habits
Smoking significantly increases your risk of various health problems, including heart disease and lung cancer. As a result, smokers consistently pay substantially higher premiums than non-smokers. This difference reflects the increased likelihood of a claim for smokers. Many insurers offer incentives for quitting smoking, potentially leading to lower premiums over time.
Policy Type
Different types of life insurance policies carry varying levels of risk for the insurer. Term life insurance, which provides coverage for a specific period, is generally cheaper than permanent life insurance (whole life, universal life, etc.), which offers lifelong coverage and a cash value component. The longer the coverage period and the more features included, the higher the premium.
Underwriting Processes
The underwriting process involves a thorough assessment of your risk profile. Stricter underwriting processes, involving extensive medical evaluations and background checks, might result in higher premiums for individuals deemed higher risk. Conversely, streamlined processes with minimal medical requirements may lead to lower premiums for those considered low risk. Different insurers have varying underwriting approaches, leading to different premium costs.
Impact of Riders and Add-ons
Riders and add-ons are extra features you can add to your policy, such as accidental death benefits or long-term care coverage. These additions increase the overall cost of your policy, as they expand the insurer’s liability. While they provide valuable protection, it’s crucial to weigh the added cost against the potential benefits.
Premium Cost Comparison for a 30-Year-Old Male
| Factor | Low Risk Profile | Average Risk Profile | High Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (30) | Baseline | Baseline | Baseline |
| Health (Excellent) | Lower Premiums | Average Premiums | Higher Premiums |
| Smoking (Non-smoker) | Lower Premiums | Average Premiums | Significantly Higher Premiums |
| Policy Type (Term Life) | Lower Premiums | Average Premiums | Average Premiums |
| Policy Type (Whole Life) | Higher Premiums | Higher Premiums | Higher Premiums |
| Riders (None) | Lowest Premiums | Average Premiums | Higher Premiums |
| Riders (Multiple) | Higher Premiums | Higher Premiums | Significantly Higher Premiums |
Policy Features and Benefits
Choosing the right life insurance policy involves understanding the various features and benefits offered. The best policy for you will depend on your individual needs, financial situation, and risk tolerance. This section will delve into the key differences between common policy types and explore the additional benefits available through riders.
Term life insurance and whole life insurance are two fundamentally different approaches to life insurance coverage. While both provide a death benefit to your beneficiaries, their structures and features vary significantly, impacting their cost and long-term value.
Term Life Insurance vs. Whole Life Insurance
The core difference lies in the duration of coverage and the investment component. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period (term), typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. Whole life insurance, conversely, offers lifelong coverage, and often includes a cash value component that grows over time.
- Coverage Duration: Term life insurance offers coverage for a specified period; whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage.
- Premiums: Term life insurance premiums are generally lower than whole life insurance premiums, especially for younger individuals.
- Cash Value: Term life insurance does not build cash value; whole life insurance builds cash value that can be borrowed against or withdrawn.
- Death Benefit: The death benefit in term life insurance remains constant; the death benefit in whole life insurance may increase over time due to cash value accumulation.
- Cost Over Time: Term life insurance premiums may increase when renewing the policy; whole life insurance premiums remain level for life.
Life Insurance Riders and Their Costs
Riders are optional add-ons that enhance the benefits of your base life insurance policy. They provide additional coverage for specific circumstances, but at an increased premium cost. The cost of a rider varies depending on the type of rider, the insurance company, and your individual circumstances (age, health, etc.).
- Accidental Death Benefit Rider: Pays an additional death benefit if the insured dies due to an accident. The additional benefit is typically a multiple of the base death benefit (e.g., double or triple indemnity). The cost is usually a small percentage increase in the premium.
- Critical Illness Rider: Provides a lump-sum payment if the insured is diagnosed with a specified critical illness (e.g., cancer, heart attack, stroke). This allows for early access to funds for treatment and related expenses. The cost depends on the specific illnesses covered and the payout amount.
- Waiver of Premium Rider: Waives future premiums if the insured becomes totally disabled. This ensures coverage continues even if the insured can no longer afford the premiums. The cost is an additional premium added to the base policy.
- Long-Term Care Rider: Provides funds to cover long-term care expenses, such as nursing home care or in-home assistance. This can help protect assets and reduce the financial burden on family members. This is generally a more expensive rider.
Comparison of Life Insurance Policy Types
The following table compares key features and benefits of three common life insurance policy types from different (hypothetical) companies. Note that actual policy features and costs will vary depending on the insurer and the individual applicant.
| Policy Type | Company | Coverage Term | Premium (Annual, example) | Cash Value | Riders Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-Year Term Life | Example Insurer A | 20 years | $500 | No | Accidental Death Benefit, Waiver of Premium |
| Whole Life | Example Insurer B | Lifetime | $1500 | Yes | Accidental Death Benefit, Critical Illness, Long-Term Care |
| Universal Life | Example Insurer C | Lifetime | Variable (adjusts based on investment performance) | Yes (investment component) | Accidental Death Benefit, Waiver of Premium, Critical Illness |
Understanding Policy Documents and Clauses
Navigating the world of life insurance policies can feel daunting, but understanding the key components of your policy document is crucial for ensuring you’re adequately protected and can make informed decisions. This section will break down the essential parts of a standard life insurance policy and explain common clauses that can significantly impact your claim.
A life insurance policy is a legally binding contract, and it’s important to carefully read and understand all its terms. Failing to do so could lead to unexpected consequences when you need to file a claim. The policy document Artikels the agreement between you (the policyholder) and the insurance company, detailing your rights, responsibilities, and the coverage provided.
Key Sections of a Life Insurance Policy
The policy document is typically organized into several sections. These sections provide essential information about your coverage and the terms of your agreement with the insurer. Understanding these sections empowers you to make informed decisions and avoid potential misunderstandings.
Common sections include the policy’s details (policy number, effective date, insured’s information), the coverage details (death benefit amount, type of policy, beneficiary designation), the premium schedule (payment amounts and due dates), and the exclusions and limitations (specific circumstances not covered by the policy). A definitions section clarifies the meaning of key terms used throughout the document. Finally, there’s usually a section detailing the procedures for filing a claim and the company’s responsibilities in the event of a claim.
Common Policy Clauses: Exclusions and Limitations
Life insurance policies often contain exclusions and limitations, which specify situations where the insurance company is not obligated to pay a death benefit. These clauses are typically designed to protect the insurer from unnecessary or fraudulent claims. Understanding these clauses is vital for making an informed decision about the policy’s suitability for your individual needs.
For example, a common exclusion might be death caused by suicide within a specific timeframe (often one or two years) after the policy’s inception. Another common exclusion might involve death resulting from participation in dangerous activities, such as skydiving or unauthorized military actions. Limitations may relate to the amount of the death benefit payable, perhaps reducing it if death occurs under certain circumstances, or placing caps on certain benefits.
Examples of How Policy Clauses Affect Claims
Let’s consider a few scenarios illustrating how specific policy clauses can affect a claim payout.
Scenario 1: A policyholder dies by suicide six months after purchasing a policy with a two-year suicide exclusion clause. In this case, the insurer might deny the claim or pay only a portion of the death benefit, depending on the specific terms of the exclusion.
Scenario 2: A policyholder, an avid scuba diver, dies during an unauthorized deep-sea dive that was not disclosed to the insurer during the application process. If the policy includes an exclusion for death related to high-risk activities not disclosed at the time of application, the insurer might deny the claim on the grounds of material misrepresentation.
Scenario 3: A policyholder dies in a car accident, and the policy has a clause limiting the payout to a percentage of the death benefit if the death was caused by driving under the influence. If it’s proven the policyholder was driving under the influence, the payout will be reduced according to the policy’s terms.
Choosing the Right Life Insurance Provider: Best Life Insurance Companies
Selecting the right life insurance provider is crucial, as it directly impacts your family’s financial security in the event of your passing. A poorly chosen policy or company could leave your loved ones with inadequate coverage or dealing with frustrating claims processes. This section provides a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process effectively.Finding the best life insurance provider involves careful consideration of your specific needs and financial situation.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer; the ideal provider depends on factors like your age, health, desired coverage amount, and budget. Taking a systematic approach ensures you find a provider that offers a policy tailored to your circumstances.
Step-by-Step Guide to Selecting a Life Insurance Provider
This guide Artikels a practical approach to selecting a life insurance provider. Follow these steps to ensure a thorough and informed decision.
- Assess Your Needs: Determine the type of life insurance (term, whole, universal, etc.) and the coverage amount that best protects your family’s financial future. Consider outstanding debts, future education expenses, and your spouse’s income. For example, a young family with a mortgage might prioritize a high coverage term life insurance policy, while a retired individual might choose a smaller whole life policy for estate planning.
- Get Multiple Quotes: Contact at least three different insurance companies to obtain quotes. Don’t just focus on the premium; consider the overall value proposition, including the policy’s features and the company’s reputation.
- Compare Policy Features: Pay close attention to policy features such as the death benefit, premium payment options, riders (additional coverage options), and any exclusions. Some policies may offer additional benefits like accidental death coverage or critical illness riders.
- Research Company Ratings and Reviews: Check independent rating agencies like A.M. Best, Moody’s, and Standard & Poor’s for the financial strength and stability of the insurance companies you are considering. Read online reviews from other policyholders to gauge their experiences with claims processing and customer service.
- Review Policy Documents Carefully: Before signing anything, thoroughly review the policy documents, including the policy contract, exclusions, and any riders. Don’t hesitate to ask questions if anything is unclear.
- Choose the Best Fit: Based on your assessment of needs, quotes, policy features, and company research, select the provider that offers the best combination of coverage, price, and reliability. Remember, the cheapest option isn’t always the best if it compromises coverage or company stability.
Questions to Ask Potential Insurance Providers
Asking the right questions is crucial to making an informed decision. This list provides essential questions to ask potential providers.
- What types of life insurance policies do you offer, and what are the key differences?
- What is the cost of the policy, and how will it change over time?
- What are the policy’s features and benefits, including riders and exclusions?
- What is your claims process, and how long does it typically take to process a claim?
- What is your company’s financial strength rating, and what does it mean?
- What is your customer service process, and how can I contact you with questions or concerns?
Comparing Life Insurance Quotes
Comparing quotes effectively involves more than just looking at the premium amount. This section Artikels a systematic approach.To effectively compare quotes, create a table that lists each company, their premium cost, policy type, death benefit, and any key features or riders. For example:
| Company | Premium (Annual) | Policy Type | Death Benefit | Riders |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | $1,000 | 20-Year Term | $500,000 | Accidental Death |
| Company B | $1,200 | Whole Life | $250,000 | None |
| Company C | $900 | 20-Year Term | $400,000 | Critical Illness |
This allows for a clear side-by-side comparison of the different options, helping you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and budget. Remember that the lowest premium might not always be the best value if the policy lacks crucial features or the company has a poor reputation.
Financial Strength and Stability of Insurance Companies
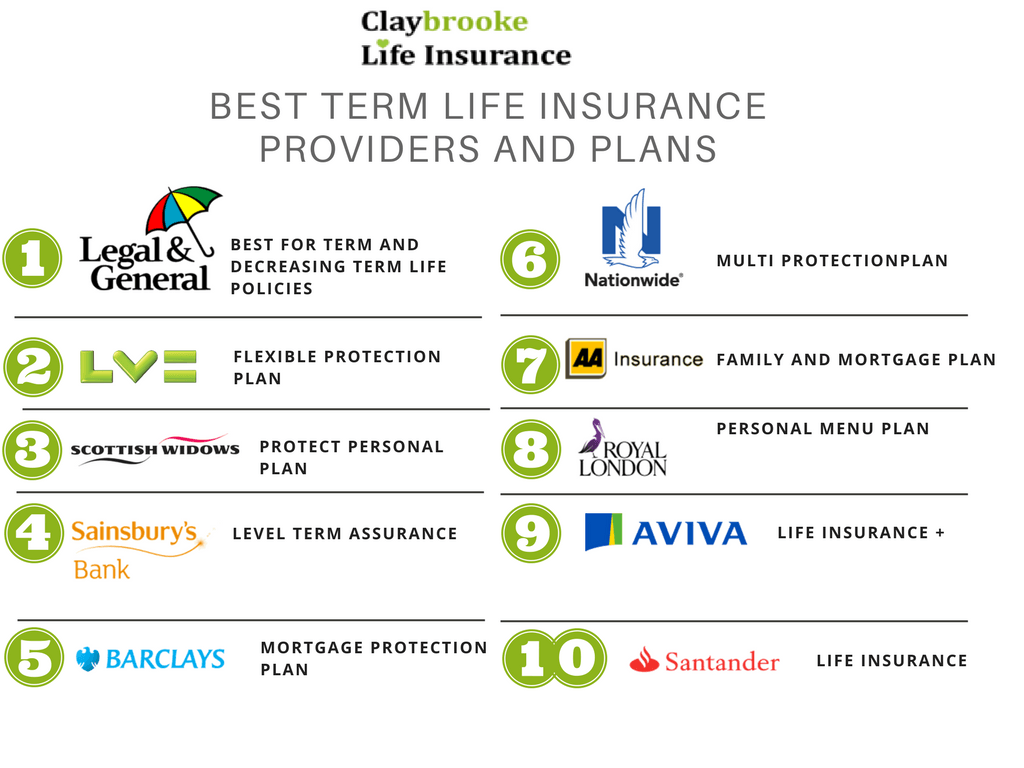
Choosing a life insurance policy is a significant financial decision, and the long-term stability of the issuing company is paramount. A company’s financial strength directly impacts its ability to pay out claims when you or your beneficiaries need them most. Understanding the key indicators of financial health is crucial for making an informed choice.Key Indicators of Financial StrengthA financially sound life insurance company demonstrates consistent profitability, strong capital reserves, and a healthy balance sheet.
Several key metrics provide insight into a company’s financial well-being. These include the company’s A.M. Best rating, a widely recognized independent assessment of insurance company financial strength; its debt-to-equity ratio, which reveals the proportion of company financing from debt versus equity; and its combined ratio, an indicator of the company’s profitability reflecting the ratio of incurred losses and expenses to earned premiums.
A lower combined ratio generally suggests better profitability. Additionally, reviewing the company’s annual reports, readily available on their websites, provides a more comprehensive understanding of their financial performance. Analyzing trends in these key metrics over several years offers a more reliable assessment than looking at a single year’s data.
Financial Health Comparison of Three Life Insurance Companies
To illustrate, let’s consider a hypothetical comparison of three companies—Company A, Company B, and Company C—based on publicly available data (note: this is a hypothetical example for illustrative purposes and does not reflect actual company performance). A bar chart visualizing this would show three bars representing each company’s A.M. Best rating. Let’s assume Company A boasts an A++ rating (the highest), Company B holds an A rating, and Company C shows a B++ rating.
A second set of bars would represent their combined ratios, with Company A showing a combined ratio of 90%, Company B at 95%, and Company C at 105%. This visual representation would clearly demonstrate the differences in financial strength and profitability among the three companies. A lower bar on the combined ratio graph indicates better profitability. The difference in A.M.
Best ratings visually underscores the significant variations in financial stability assessments by independent rating agencies.
Importance of Considering Financial Strength, Best life insurance companies
Selecting a life insurance policy is a long-term commitment. The policy’s value hinges on the insurer’s ability to fulfill its obligations when a claim arises, potentially decades into the future. A financially weak company risks insolvency, leaving policyholders with unpaid claims. Therefore, prioritizing a company with a proven track record of financial stability and a high rating from reputable agencies is crucial.
Choosing a financially strong company provides peace of mind, ensuring your beneficiaries receive the promised benefits when needed. This diligent approach minimizes the risk of financial loss and ensures your loved ones are adequately protected.
Closing Notes
Securing your family’s financial well-being through life insurance is a significant responsibility. This guide has provided a framework for understanding the key aspects of choosing the best life insurance company and policy for your circumstances. Remember, comparing quotes, understanding policy features, and assessing the financial strength of the insurer are all critical steps in making an informed decision. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice if needed; taking the time to thoroughly research and understand your options will ultimately provide you with peace of mind knowing you’ve made the best choice for your loved ones.
FAQ Summary
What is the difference between term and whole life insurance?
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period (term), typically 10, 20, or 30 years, at a fixed premium. Whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage with a cash value component that grows over time.
How often are life insurance premiums reviewed?
That depends on the type of policy. Term life insurance premiums are usually fixed for the policy term. Whole life premiums are typically level (remain the same) throughout your life. Some policies may adjust premiums based on your age or the insurer’s financial performance.
Can I change my beneficiary after purchasing a policy?
Yes, most life insurance policies allow you to change your beneficiary at any time. The process typically involves submitting a written request to the insurance company.
What happens if I miss a premium payment?
Missing a premium payment can lead to your policy lapsing (becoming inactive). Most insurers offer a grace period (usually 30 days) to make the payment before the policy lapses. However, after the grace period, your coverage may be terminated, and you may lose any cash value that has accumulated (if applicable).
What are the implications of not disclosing pre-existing conditions?
Failing to disclose pre-existing medical conditions during the application process is considered misrepresentation and could lead to your claim being denied or your policy being canceled. Be completely honest and accurate when applying for life insurance.